Diabetic Retinopathy - Introduction
Diabetic retinopathy is only one of the complications of diabetes mellitus. It may occur even if the diabetes disease is held under control. If left untreated diabetic retinopathy may eventually lead to severe loss of vision and blindness. Patients suffering from diabetes may apart from diabetic retinopathy also develop cataract and glaucoma.
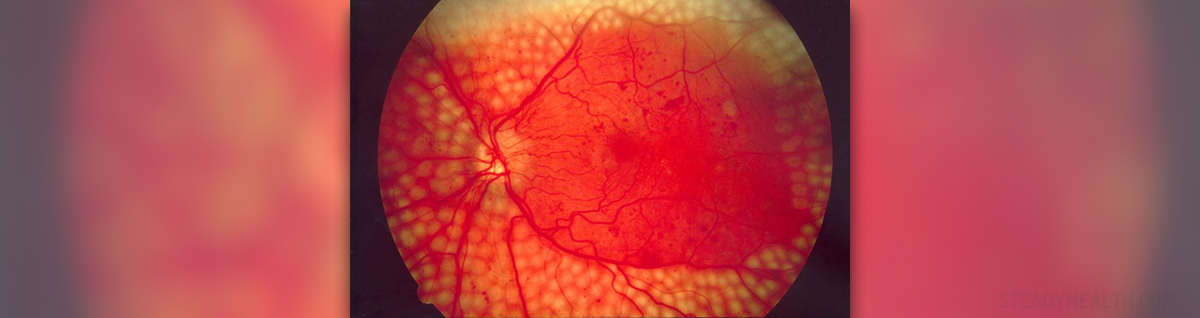
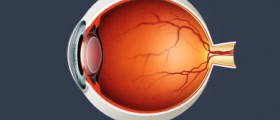
In diabetic retinopathy the changes include swelling of the retinal blood vessels and leakage of the fluid or abnormal growth of new blood vessels on the surface of the retina. This interferes in normal vision and requires prompt therapy. There are four stages of diabetic retinopathy and they include mild nonproliferative retinopathy, moderate nonproliferative retinopathy, and severe nonproloferative retinopathy and finally, the fourth stage is proliferative retinopathy.
Causes and Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy
The loss of vision occurs as a consequence of two processes. In the first process the fragile and abnormal blood vessels which tend to develop lead to leakage of the blood into the centre of the eye. This results in blurred vision. The fluid can leak into the center of the macula and cause its swelling which also results in blurred vision. Swelling of the macula is medically known as macular edema and it affects many patients suffering from diabetic retinopathy. And the second process which causes problems with vision is formation of new blood vessels in the retina. Their presence can significantly interfere with normal vision.
Diagnosing Diabetic Retinopathy
In the beginning of the disease there are no symptoms at all. This is why all patients suffering from diabetes are due to go for regular check-ups at their ophthalmologist. This way the disease can be diagnosed on time.
The diagnosis can be easily set after the doctor (ophthalmologist) performs a dilated eye exam. Additional tests include visual acuity test and tonometry. The ophthalmologist will look for leaking blood vessels in the retina, the presence of retinal swelling (macular edema), pale fatty deposits on the retina, damaged nerve tissue and any change in blood vessels including the occurrence of new blood vessels.
Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy
First three stages of diabetic retinopathy are not treated. Only in case of macular edema patients require proper treatment.
The last stage of diabetic retinopathy is treated with laser surgery. The goal of the surgery is to shrink the abnormal blood vessels. The patient must participate in two or more sessions so that the results can be satisfying enough. Macular edema is also treated with laser surgery. This procedure is called focal laser surgery and is performed in only one session. And finally, if there is blood in the centre of the eye, to be more precise inside the vitreous gel the patients must undergo a vitrectomy.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...