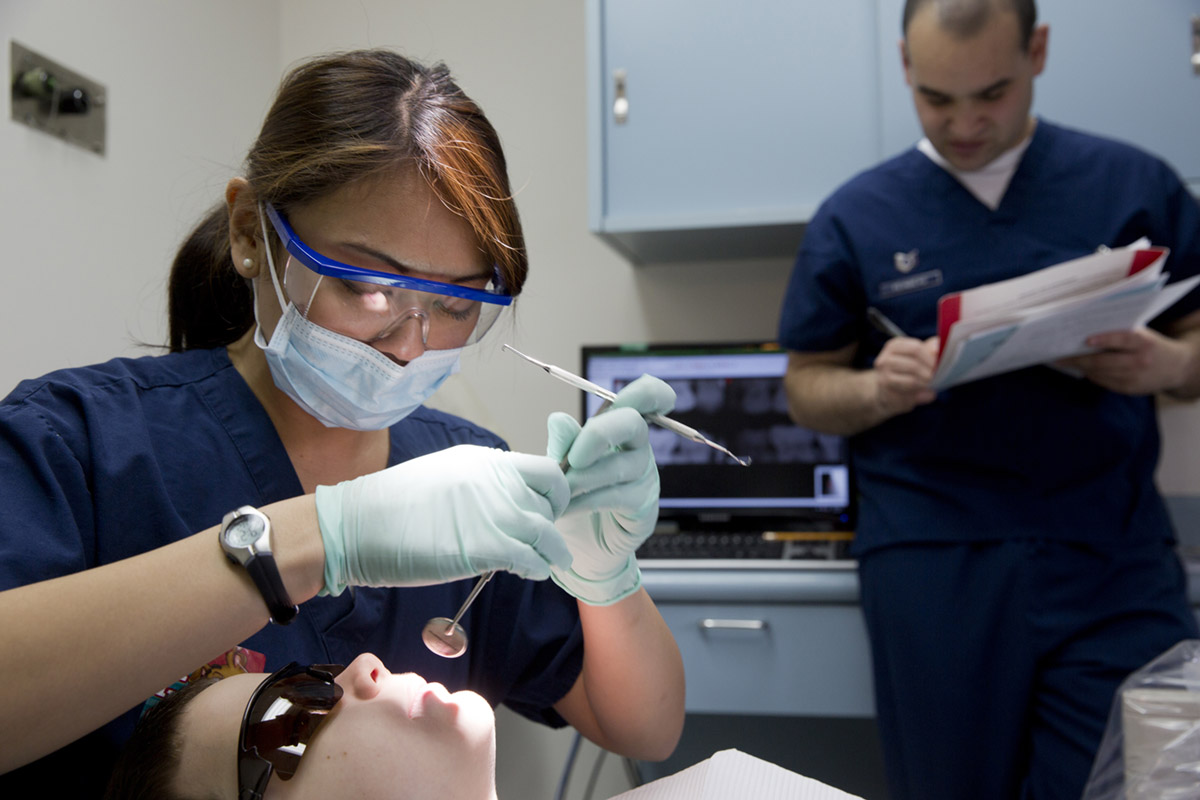
Crossbite can be defined as occlusal irregularity in which teeth from the upper and lower jaw do not correspond. Normally these teeth occlude. Crossbite is a consequence of misalignment of teeth in upper or lower jaw. This is a common dental problem for many children as well as adults.
Crossbite can affect one tooth or a group of teeth. There are several types of crossbite, anterior, posterior (bilateral and unilateral). Anterior crossbite is actually typical for class III skeletal relations. Posterior crossbite is associated with a narrow maxilla and upper dental arch. Posterior cross bite can be further classified as unilateral or bilateral. Unilateral crossbite features with a lateral shift of the mandibula and in case it is not treated properly and on time it may develop into a structural shift and subsequent skeletal asymmetries.
Crossbite in Children: Causes
A variety of factors contribute to crossbite in children. The first issue is to identify whether the problem is skeletal or dental. In case of skeletal nature of crossbite it is most commonly connected to a small upper jaw, a large lower jaw or a combination of the two. If this is the case the child may be suffering from congenital micrognathia of the upper jaw (abnormally small upper jaw and normal size of the lower jaw). These children generally suffer from both types of crossbite, anterior and posterior.
If crossbite is solely dental it is associated with misaligned teeth. The problem is either lesser space in the jaws or crowding teeth. Children who are prone to mouth breathing, which leads to an increase in the length of the face that subsequently causes shifting of the occlusion distally i.e. backwards. Dental crowding features with misalignment of the teeth where affected teeth move slightly anterior or posterior to their normal position in the jaw. Misalignment is here a consequence of insufficient space. This particular problem may be also a consequence of premature extraction of milk teeth and eruption of permanent teeth.
Crossbite in Children: Treatment
The treatment of crossbite in children depends on the actual cause (skeletal or dental) of the problem. Skeletal problems generally require a surgical correction with one goal- correction of the skeletal deformity. If crossbite is dental in nature patients undergo orthodontic treatment which includes placing orthodontic braces in the mouth. The braces are connected with tightening wires and the teeth are eventually brought into their normal position. Some cases of crossbite in children require both, surgical correction and orthodontic treatment.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...