Corneal Abrasion Healing Time
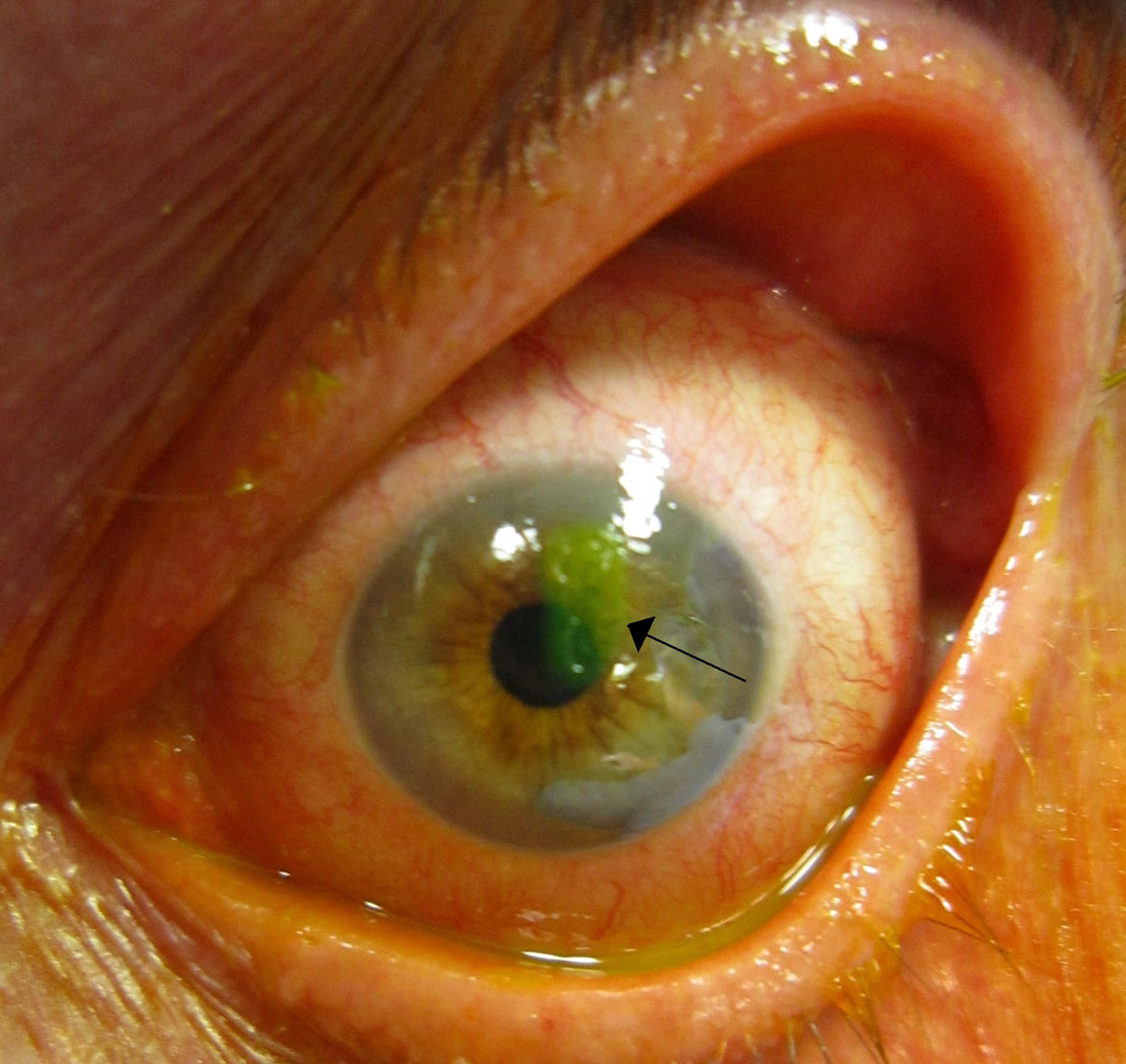
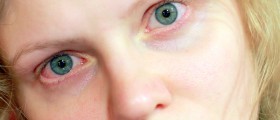
The medical term for a scratched cornea is corneal abrasion. This happens when a person damages the surface of the epithelial layer of the cornea somehow. A person who has damaged the cornea may also experience epithelial defects and corneal edema as well. However, more common symptoms are eye pain, a feeling that there is some foreign object in the eye, swollen eyelids and blurred vision. The treatment does not last for too long but the healing time may be from 7 days to a whole year. It all depends on the seriousness of the damage.
Corneal abrasion causes
There are plenty of reasons how a person may damage the cornea. However, the most common is the intrusion of a foreign object in the eye. This foreign object may be a sand particle or it can be a branch of a tree which has grazed the eye. These foreign objects in the eye can make even more damage of the eye if they are not taken out on time. They will also prolong the healing time of the cornea. Apart from these intrusions of foreign objects a person can damage the cornea via some eye infection and even exposure to ultraviolet light.Corneal Abrasion Treatment
However, in case of a recurrent abrasion, a person may need to undergo a laser eye surgery. This is because the surgery will cure different ocular disorders. The name of the surgery is phototherapeutic keratectomy. Even though cases when corneal abrasion leads to corneal ulcer are pretty rare they do happen. When this happens a person will have to undergo a corneal transplant in order to restore vision.
- The goals of treatment are to relieve pain, prevent bacterial superinfection, and speed healing. Options include oral analgesics, as well as topical agents, such as antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and cycloplegics. Few treatments have been evaluated in controlled trials, and many recommendations are based on theoretical benefit and general consensus.
- Options for pain relief include oral analgesics, topical NSAIDs, and, occasionally, topical cycloplegics. Oral analgesics such as acetaminophen and NSAIDs may be sufficient to relieve pain. In more severe cases, opioid analgesics may be necessary. Topical NSAIDs (e.g., diclofenac 0.1% [Voltaren], ketorolac 0.4% [Acular LS]) have been shown to relieve pain, decrease the need for oral analgesics, and provide earlier return to work without delaying healing or increasing the risk of infection. Topical NSAIDs should be used only in uncomplicated corneal abrasion and for no more than one to two days, because prolonged use may be associated with corneal toxicity. Because topical NSAIDs are more expensive than oral analgesics, physicians should take cost into consideration when discussing treatment options with patients.
- In patients who wear contact lenses, the eyes are often colonized with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other gram-negative organisms. After a corneal abrasion, bacterial superinfection can rapidly progress to perforation of the cornea and permanent vision loss. Therefore, these patients should be prescribed a topical antibiotic with antipseudomonal activity, such as a fluoroquinolone or an aminoglycoside. The use of these agents should be limited to contact lens–related abrasions because of evidence of increasing fluoroquinolone resistance and potential toxicity of aminoglycosides to the corneal epithelium.
- Young children may not be able to explain symptoms such as foreign body sensation. Thus, a penetrating injury should be suspected in any child who is reluctant to open his or her eye. The inner surface of the lids should be examined for foreign bodies, and it is prudent to routinely sweep these surfaces with a moistened cotton swab. Because topical antibiotic solutions may sting, ointments are preferred.
- Most uncomplicated corneal abrasions heal in 24 to 48 hours. Follow-up may not be necessary for patients with small (4 mm or less), uncomplicated abrasions; normal vision; and resolving symptoms. Follow-up in 24 hours is indicated for other patients, including those with larger abrasions (greater than 4 mm), contact lens–related abrasions, and diminished vision.
Corneal abrasion healing time
In most cases, the abrasion will be cured in a matter of a couple of days but it will depend on the severity of the injury. It is important that the person is very careful not to damage the eye further while recovering. This means that physical activities are out of the question. An important thing to remember is that hands must be clean whenever a person touches the eyes and that he or she should not share eye medications.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...