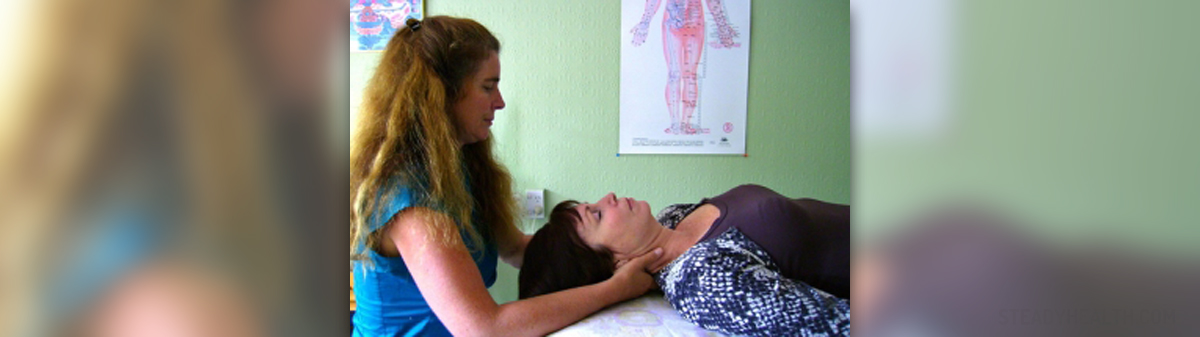
Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Myofascial Pain
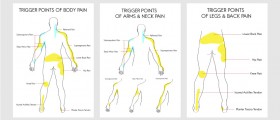
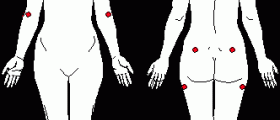
The most typical symptom of the condition is pain triggered by touching specific tender points. By touching these points the muscle twitches and this results in intensive pain. It is possible to touch certain trigger points and yet to feel pain in another area of the body. This pain is called referred pain.
It is essential to make a difference between chronic myofascial pain and fibromyalgia. Namely, in patients suffering from chronic myofascial pain there is a direct impact on the affected muscles and fascia while in fibromyalgia the problem is believed to originate from a dysfunction of certain chemical substances. Furthermore, patients suffering from fibromyalgia complain about generalized aching and the pain in chronic myofascial pain remains relatively localized.
All trigger points are divided into active trigger points and latent trigger points. If the trigger point is active, it is always sensitive and sore and never allows the specific muscle to be used completely which eventually results in muscle weakness and reduction in range of motion. On the other hand, latent triggers are only tender when touched and may activate when the specific muscle is injured or strained.
Causes of Chronic Myofascial Pain
Experts have not managed to identify the actual cause of chronic myofascial pain yet. Still, many of them assume that the condition has something to do with having one leg longer than the other (poor posture), stress and excessive use or muscles. Even poor techniques of exercising may trigger the pain. Depression and anxiety are two more potential contributors to chronic myofascial pain. And finally, the problem may develop as a result to direct trauma, fatigue and exposure to cold.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Chronic Myofascial PainAfter taking a medical history, proper physical examination, additional tests and exams a doctor can rule out other condition and then confirm that an individual is suffering from chronic myofascial pain.
Treatment includes physical therapy, some medications and massage therapy. Physical therapy is essential part of treatment for chronic myofascial pain and it includes stretching exercises, postural and strengthening exercises. Medicamentous treatment includes NSAIDs and sometimes injections of local anesthetics (when the pain is unbearable). And finally, proper massage technique can loosen tight muscles and eliminate cramping and muscle spasms.


-vs-Trigger-Points-(Myofascial-Pain-Syndrome)_f_280x120.jpg)











Your thoughts on this
Loading...