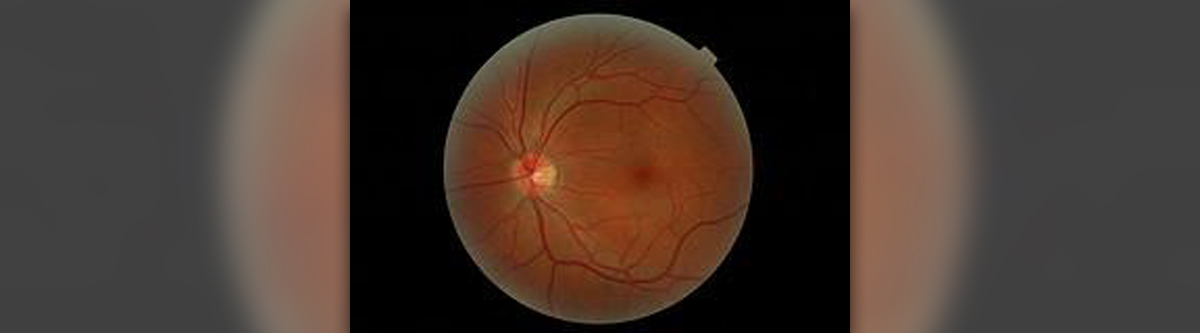
Central serous retinopathy (CRS) is an eye disorder characterized by fluid build-up under the retina of the eye. This accumulation is a reason why patients typically complain about problems with their vision in dim light, especially in an oval shaped gray or brown area. Their vision is also blurry while the images their eyes receive become severely distorted.
Impaired Eye Vision
The build-up of fluid under layers of the retina may cause serious vision problems and eventually cause retinal detachment, a medical emergency. The accumulation develops due to the presence of small breaks in the retinal pigment endothelium. The reason why these breaks occur and why the condition develops remain unknown. So, practically serous central retinopathy is classified as idiopathic medical condition. However, extensive research has confirmed that there are certain risk factors that might precipitate fluid build-up and subsequent retinal detachment. For example, women are affected more than men and the problem tends to be more frequent at around age 45. What is more, stress is one of potential contributors to central serous retinopathy. Namely, certain studies have confirmed that aggressive individuals (known to have 'type A' personality), particularly if they are under a lot of stress easily end up with the condition. And finally, prolonged intake of steroids is associated with fluid build-up under the retina, therefore might be a potential cause of serous central retinopathy.
As for the outcome of the disease, it generally lasts for a few weeks although some individuals might have visual issues that linger for months. The symptoms fluctuate during the day and even on an hourly basis. Stress, exhaustion and illnesses make symptoms become more intensive.
One of the major problems regarding serous central retinopathy is its recurrence. It leads to severe damage to the organ. Also, the more episodes of central serous retinopathy people experience, the greater is the chance they will develop retinal detachment. Once the detachment occurs, some layers of the organ become deprived of blood and all the essential nutrient which affects the function of the retina in the long run. Such individuals report the presence of permanent gray area in the field of vision or a blind spot. Recurrence of the disease is reported to occur more in people who have had a severe initial attack of the disease.
All in all, the prognosis of central serous retinopathy is quite good. Approximately 90% of all patients restore 20/30 vision or even more within a half of the year. Progressive vision loss is typically associated with recurrent attacks of fluid build-up.
How is Central Serous Retinopathy Managed?
Unfortunately, medical experts have not managed to identify a successful treatment approach for this particular medical condition. Some of them experimented with laser. Research results, however, do not confirm that this treatment approach might provide with improvement in the long run. Now, laser is a very powerful tool used in many different types of retinopathy especially those in which there are new blood vessels forming inside the retina. Its inefficiency in case of central serous retinopathy might be explained by the lack of such neovascularization and solely the presence of fluid build-up. However, laser may close the tiny breaks in the organ, preventing further fluid accumulation. Lasers are used in acute form of the disease and sometimes even a couple of months after the attack when they might prevent permanent damage to vision.
Since the hypothesis of central serous retinopathy being associated with stress may be correct, we should also take into consideration stress and the onset of the disease or its recurrent episodes. Namely, as it has already been mentioned people who are under stress are prone to central serous retinopathy. Stress per se stimulates the adrenal cortex to synthesize cortical, the hormone blamed for many changes in the body which are a part of a normal stress reaction. Now, such excess of cortisol might precipitate central serous retinopathy. Excess of cortisol is found in patients who are treated with corticosteroid due to some other medical condition. There has been certain number of people treated with corticosteroids who eventually developed central serous retinopathy. As soon as the drugs have been discontinued the condition affecting the eye resolved.
The excess of cortisol is also confirmed to exist during pregnancy. Its role is to prevent damage caused by abrupt and every day changes a woman's body is going through. So, this might explain why central serous retinopathy statistically attack women more than men.
In spite of all the mentioned scientists need to focus more and engage in many studies in order to definitely identify and confirm the underlying cause of central serous retinopathy. At the moment they probably explore new treatment options and give their best to find the best solution to the problem. In the meantime, we all should leave stress aside because its role in the onset of central serous retinopathy as well as many other highly detrimental medical condition seems to be immense.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...