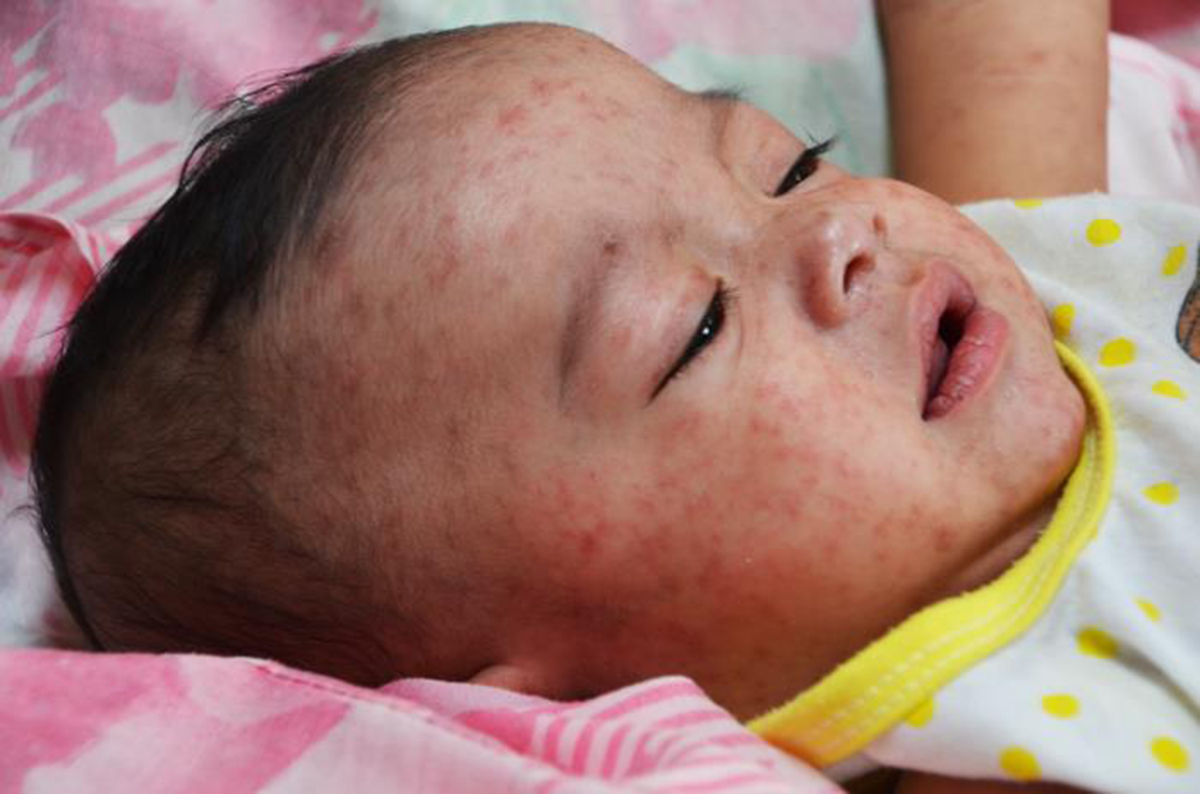
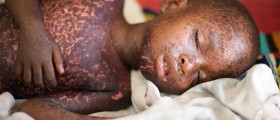
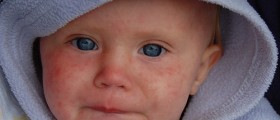
Measles
Causes of measles and spreading
This disease is caused by paramyxovirus of Morbillivirus genus. It is spread through respiration. For example, if an infected person sneezes or coughs, millions of tiny droplets that come out contain the virus. If a healthy person comes in contact with the droplets directly, or by touching an object on which they landed and then touching mouth or nose, he or she will contract the virus.
The measles virus can survive outside the body, for example on surfaces, for several hours.
Once the virus enters the body, it starts to multiply in the throat and in the lungs, and then it spreads throughout the body, affecting lungs and skin.
A person who has contracted the virus is infectious two to four days before the symptoms appear and five days after they appear, which means that in that period they can infect other persons.
Not everyone can get infected. Generally, it is almost impossible for persons who have had measles to get infected again. This is because the body develops immunity to measles, which protects the person virtually forever.
This disease is highly contagious. It is estimated that a person who has not had measles has 90 percent chance of getting infected if sharing the house or workspace with an infected person.
This is why, most cases of measles occur in young children and rarely in adults.
Treatment and prevention
In most cases measles do not require specific treatment. Doctors recommend bed rest, healthy diet and over-the-counter medication for the symptoms, for example ibuprofen or Aspirin for fever and pain.
However, it is possible that measles cause complications like pneumonia, ear infections, eye infections and croup. When this happens, it is necessary to see a doctor who will prescribe adequate treatment for the specific complication.
More serious complications are rare but they are possible. Encephalitis as a complication of measles, which may be fatal, is responsible for hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide.
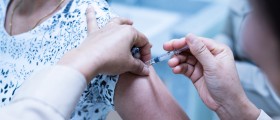
Measles can be prevented with MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine. This vaccine is usually given to children who have 18 months, because it is believed that before this age they are protected by the mother’s immunity. The second vaccination is given between ages four and five, in order to increase immunity.
This vaccine is highly effective and generally safe, although there have been some speculations that link it to autism. Those speculations have not been confirmed.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...