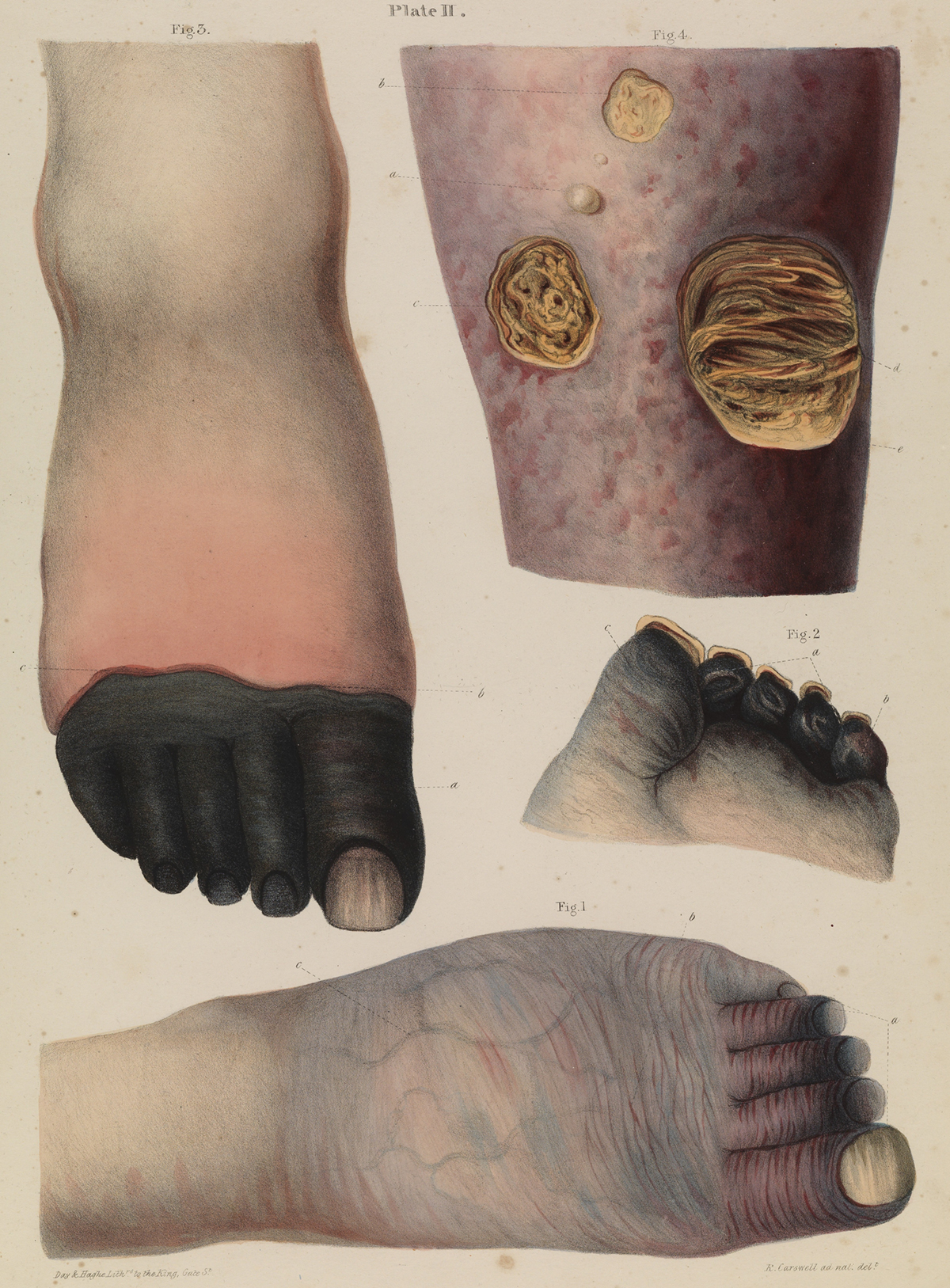
Gangrene is a severe condition that arises when a considerable mass of bodytissue dies (this is known as necrosis). It develops when the bloodsupply to the affected part is cut off as a result of various processes, suchas infection, vascular (pertaining to blood vessels) disease, or trauma.Gangrene can involve any part of the body; however, the most common sitesinclude the toes, fingers, feet, and hands.
There are two major types of this condition: dry gangreneand wet gangrene.
Dry gangrene is caused by a reduction of blood flow throughthe arteries. It appears gradually and progresses slowly. In most people, theaffected part does not become infected.
Wet gangrene develops as a complication of an untreatedinfected wound. There is also a subtype of wet gangrene calledgas gangrene (it is caused by the bacteria known as Clostridia).
Causes of Gangrene
The common cause of gangrene is loss of an effective localblood supply to any tissue. This means that the tissues are deprived of oxygen,thus causing the cells in the tissue to die. The most common causes of tissueblood supply loss are infections, trauma, and diseases that can affect bloodvessels (usually arteries).
Any process that affects blood flow (such as an injury oran underlying condition, or especially a combination of the two) can lead togangrene.
There are several risk factors that might increase one’s chancesof getting gangrene. These are: blood vessel disease, severe injury, diabetes,etc.
Gangrene Symptoms
The most common symptoms of are: severe pain followed by a feeling of numbness,blue (or black) discoloration of the affected skin, and a foul-smellingdischarge leaking from the sore.
In gas gangrene, additional symptoms may be swelling, fever, and feelingunwell.
A condition called septic shock can occur if abacterial infection that originated in the gangrenous tissue spreads throughoutthe body. Symptoms of septic shock are: lightheadedness, confusion, rapid heartrate, and low blood pressure, etc.
It is vital that one consult a doctor as soon as he hasnoticed these symptoms. Gangrene, if left untreated, can cause severalcomplications, such as scarring and need for reconstructive surgery. If thetissue damage is so severe, a part of the body must be removed. Also, gangrenecan lead to damage to other organs, and the result may be fatal.
Treatment
Treatment of gangrene depends upon the type of gangrene, thesubtype of wet gangrene, and upon how much tissue is compromised by the disease.
Early gangrene treatment is essential to prevent the risksof severe infection and localized spreading of the dead tissues.
Dry gangrene treatment.Treatment forthis type of gangrene usually involves restoring the blood vessels affected.The doctor may also suggest a surgery to repair the damage.
Wet gangrenetreatment.The doctor may consider an intravenous antibiotic injection as the firsttreatment approach. Also, it prevents further bacterial infections. The deadtissue is removed with a surgical procedure.
Gas gangrene treatment.In thetreatment of gas gangrene antibiotic injections followed by surgicaldebridement are followed. An alternative method is hyperbaric oxygen therapy.This helps the healing of the tissue.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...