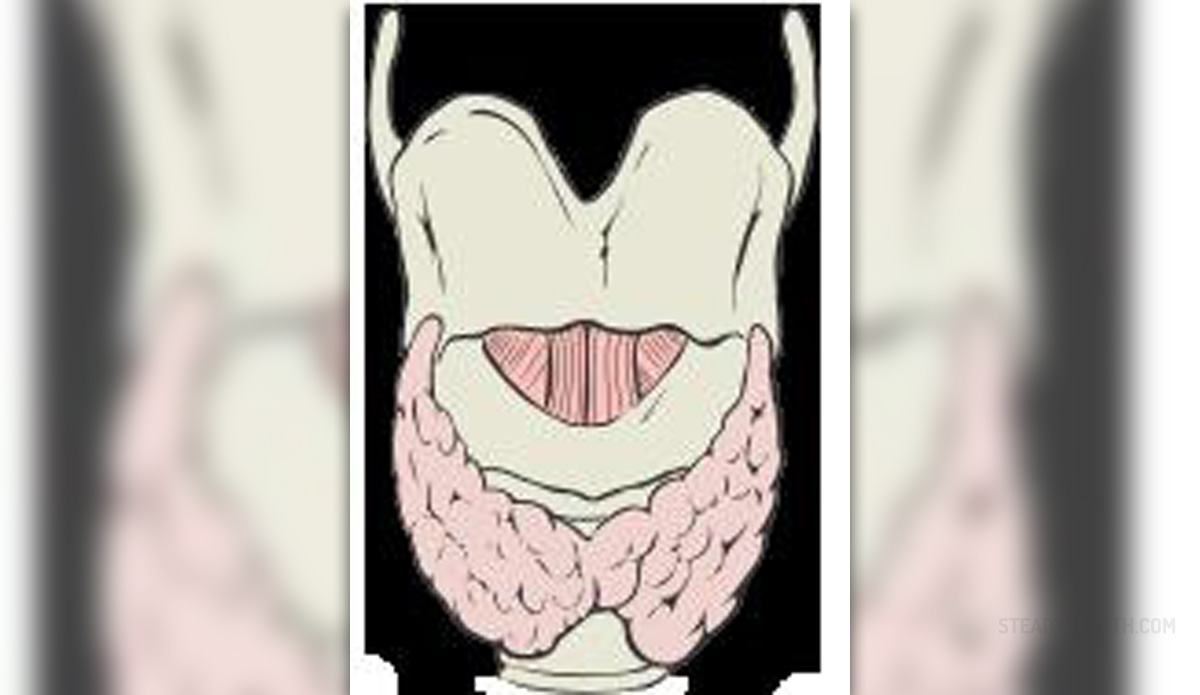
Thyroiditis is, by definition, inflammation of the thyroid gland. Autoimmune thyroiditis is only one type of this inflammation. It develops as a consequence of the attack of antibodies produced by the body. Namely, in such case the body produces antibodies which do not recognize thyroid cells and attack them. This eventually leads to severe damage to the gland and requires adequate treatment.
Autoimmune thyroiditis is also known under the names Hashimoto's thyroiditis and chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. It predominantly affects women, particularly middle-aged women, and may run in families.
Clinical Characteristics of Autoimmune Thyroiditis
The problem of autoimmune thyroiditis is that it may last for a long period of time and still be asymptomatic. This is a huge issue since progression of the disease leads to severe damage to the thyroid gland and may eventually result in hypothyroidism.
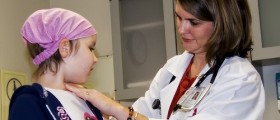
However, if there are symptoms and signs of autoimmune thyroiditis they generally include neck enlargement (goiter), low appetite, weight gain, constipation and problems with concentration and thinking. Fatigue, dry skin, hair loss (dry and coarse hair), joint pain and stiffness, muscle pain and weakness, trembling hands and excessive sweating are several more characteristics of autoimmune thyroiditis. Women may have irregular and heavy periods. Such patients are susceptible to infections and may suffer from high level of cholesterol. And finally, some of them develop depression. If any of the mentioned symptoms or signs occur, a person is due to consult his/her health care provider.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Thyroiditis
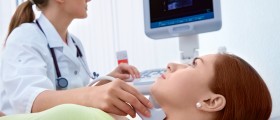
The definitive diagnosis is set after evaluation of all symptoms and signs and physical exam. Doctors additionally perform blood and urine analysis and check the level of thyroid hormones in the body. Patients undergo ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Definitive conformation can be achieved if there are antibodies in blood or after pathohistological examination of the samples taken during thyroid gland biopsy.
Treatment for Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Since autoimmune thyroiditis leads to damage of the thyroid gland it is no wonder that most patients eventually develop hypothyroidism. They require proper thyroid hormone replacement therapy for the rest of their lives. Optimal amounts of thyroid hormones are achieved with drugs such as levothyroxine. This drug can be also administered in patients suffering from subclinical hypothyroidisms (mild symptoms of hypothyroidism and slightly elevated levels of TSH). It is recommended to monitor patients and start with hormone replacement therapy only when the level of thyroid hormones drops.
Finally, it is essential to mention that people suffering from autoimmune thyroiditis are also susceptible to other autoimmune disorders. In rare cases such patients may develop thyroid cancer.








-And-Children-16-Warning-Signs-And-Symptoms_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...