
What is nummular dermatitis?
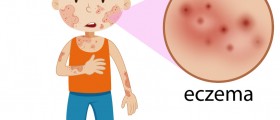
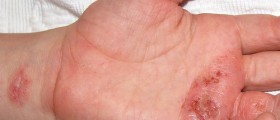
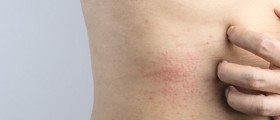
Nummular dermatitis, also called discoid eczema and nummular eczema, is a form of eczema characterized by round or oval plaques forming on the skin, usually on the arms and legs. It does not seem to be genetic or inherited, it is not related to food allergies and it is not contagious.
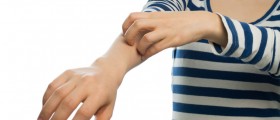
These lesions usually starts as papules, progressing to scaly plaques. The plaques are usually very itchy, and, if scratched, the skin may break.
Nummular dermatitis is often accompanied by xerosis or dry skin. It may even start as a patch of dry skin that evolves into lesions and then into plaques with scale. Dry skin is usually caused by problems with oily barrier of the skin. When the skin is dry, it is more permeable and thus more prone to allergens. If the allergens come into contact with the skin damaged in that way, they cause an irritant or an allergic response.
Causes of nummular dermatitis
The onset of nummular dermatitis, which is often chronic and recurrent, can be associated with certain medications. Severe nummular dermatitis was seen in people who took interferon and ribavarin prescribed for hepatitis C. This skin condition is also associated with inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor.
Nummular dermatitis may also have something to do with mercury used in dental fillings. It is believed that hypersensitivity to metals is able to induce an immune reaction in form of skin lesions and nummular plaques.
Several studies have also focused on the role of neurogenic contributors in inflammation characteristic for nummular dermatitis and atopic dermatitis.
Certain factors have been identified as triggers for nummular dermatitis. Those include stress, caffeine, dehydration and basically anything that causes skin dryness.
Treatment for nummular dermatitis
Nummular dermatitis is usually chronic and recurrent. This means that there is no specific treatment that would cure it forever. The best thing one can do is to try to prevent flare-ups and to make them more tolerable if they appear. As for the prevention, the most effective way is to keep the skin moisturized at all times, using high-quality hypoallergenic skin moisturizers. Moisturized skin is much less likely to have flare-ups of nummular dermatitis.
Topical corticosteroids can be used for outbreaks when they occur. Oral antihistamines can be used to relieve itching, which is very useful since scratching the plaques can aggravate the problem even more.
It is important to make sure the affected skin does not become infected, for example with staphylococci. In case that happens, it is necessary to use topical and/or oral antibiotics.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...