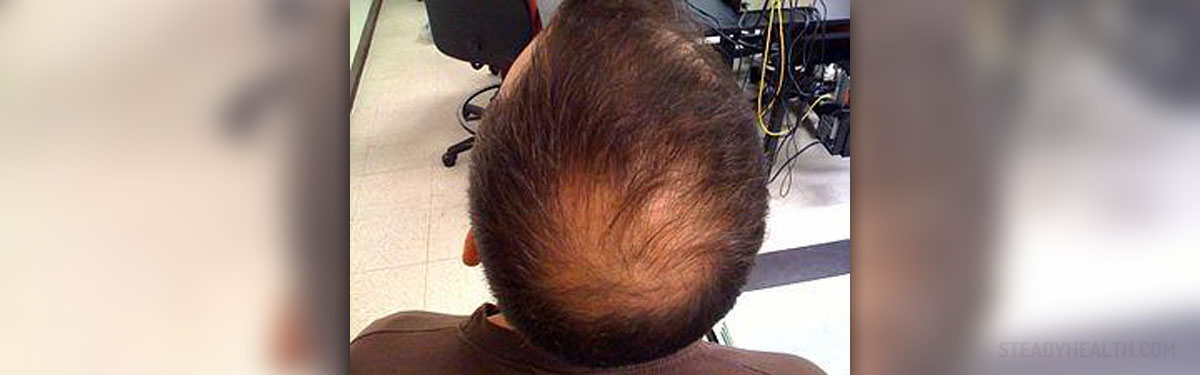
Alopecia areata is not a life threatening condition but it is a major aesthetic problem for both, males and females. This is a skin condition that develops in a form of patchy hair loss. Initially, there are many bold patches on the head. However, progression of the disease may eventually cause complete baldness.
Alopecia Areata Causes and Risk Factors
The actual cause of alopecia areata remains unknown. Still, in around a fifth of all patients there is a positive family history of the condition. This drives to conclusion that the condition may be inherited.
Furthermore, some scientists believe that alopecia areata develops due to abnormal immune response of the body. This theory classifies alopecia areata into autoimmune illnesses.
Finally, the onset of the disease is sometimes connected with a major life event such as an illness, pregnancy or trauma. Alopecia areata affects both women and men and people of all ages.
Alopecia Areata Clinical Characteristics
There are no additional signs or symptoms of the condition apart from obvious hair loss. In alopecia areata the hair sheds in a form of bald patches. The condition is in majority of cases located to the scalp although it may also affect the eyebrows, beard, arms or legs. The hair loss is in a form of roundish, smooth peach-colored patches. Certain number of patients may complain about itchy and burning sensation of the affected skin.
Alopecia Areata Treatment
It is possible for the condition to resolve on its own and hair may start growing again within a period of one year even if the affected individual is not treated. However, after diagnosing alopecia areata doctors most commonly opt for some treatment which can be either conservative or surgical.
Medicamentous treatment is effective in some patients. Many factors (e.g. the amount of hair loss, person's reaction to hair loss etc.) determine whether drugs will be efficient or not. Minoxidil is a drug widely used in patients suffering from alopecia areata. The drug is in a liquid form and is rubbed directly into the scalp.
Corticosteroids and Anthralin
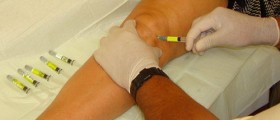
Another treatment option fro alopecia areata are injections of corticosteroids. This treatment is a bit painful because injections are applied directly into the affected skin. Corticosteroid may also be applied in a form of creams or ointments, but these are not as efficient as injections.
Anthralin is a drug available as a cream/ointment. It works only when it is regularly applied onto the affected area. Discontinuation of the treatment influences further hair growth.
Surgery
Finally, surgery is the last resort for individuals who have not responded to conservative treatments. Hair transplant surgery and scalp reduction surgery are two surgical options for individuals suffering from alopecia areata.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...