
ADD inChildren
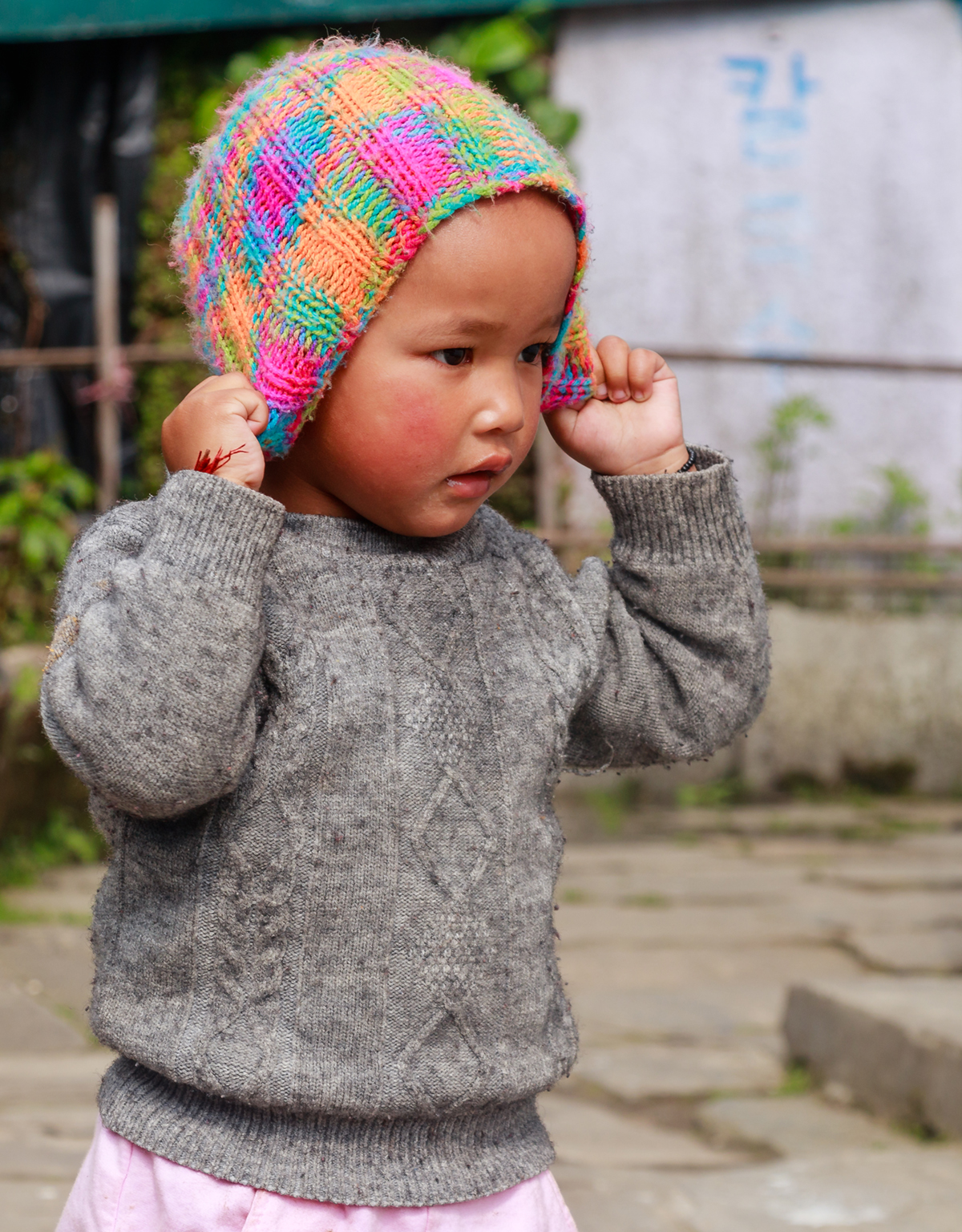
AttentionDeficit Disorder (ADD) is the name for a combination of conditionsthat cause a person to lose their focus quickly and impairs theirconcentration. It also results in emotional fluctuations and otherissues with sociability.
Childrenaffected by ADD will suffer from a lack of concentration,particularly in school or while having conversations. Teachers ofsuch children will sometimes view this as a lack of consideration forthe school work or simple disobedience. This will cause problems forthe child, as they will not be able to adequately complete homeworkor projects, leading to disappointing grades. Adults with ADD will besimilarly affected in their careers or relationships.
Symptomsof ADD in children do not usually appear in one go, but rather over along period of time, typically a few months. If these are notcontrolled correctly, they can become worse over time, oralternatively the child may believe that his behaviour is normal andconsciously attempt to act in those ways.
ADD isdifferent from ADHD (the H standing for 'hyperactive') in that thechild is simply inattentive and not also over-energetic. Whenengaging in an enjoyable activity, the child may seem completelyfine, but symptoms typically appear when they are trying to learnsomething new or they are engaging in an activity that they do notlike.
No twoindividuals show the same symptoms of ADD; while one may be extremelypassive, another may be aggressively hyperactive. Male children aretypically more prone to ADD than females, although this may just bedue to the natural behaviour patterns of male children that aremisconstrued as ADD symptoms. ADD is apparent in around 2-5% ofchildren in the United States, and most children do not grow out ofthe condition, exhibiting symptoms throughout their lives. The bestoutcome is that the symptoms are identified in the child very earlyon and appropriate care can be instituted immediately to have more ofan effect as the child grows older.
Signsof ADD
Thefirst signs one should notice in their infant is incessant screamingor crying, insomnia, restlessness, tantrums and reluctance toaffection from parents. In older children, typical symptoms includerecklessness or impulsiveness, aggression and lack of hand-eyecoordination. Poor performance in school despite a high IQ is anotherstrong indicator. Mood swings, sleeplessness, poor motor skills andpoor appetite are also major signs to watch for. Some children maydisplay physical symptoms, including sensory hypersensitivity,swollen neck glands or wetting of the bed.
Someof these symptoms are merely exaggerated mannerisms common in allchildren. Careful monitoring of the degree of the symptoms is the key todetermining if a child is possibly affected by ADD. Consult a medicalprofessional for advice if unsure.






-And-Children-16-Warning-Signs-And-Symptoms_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...