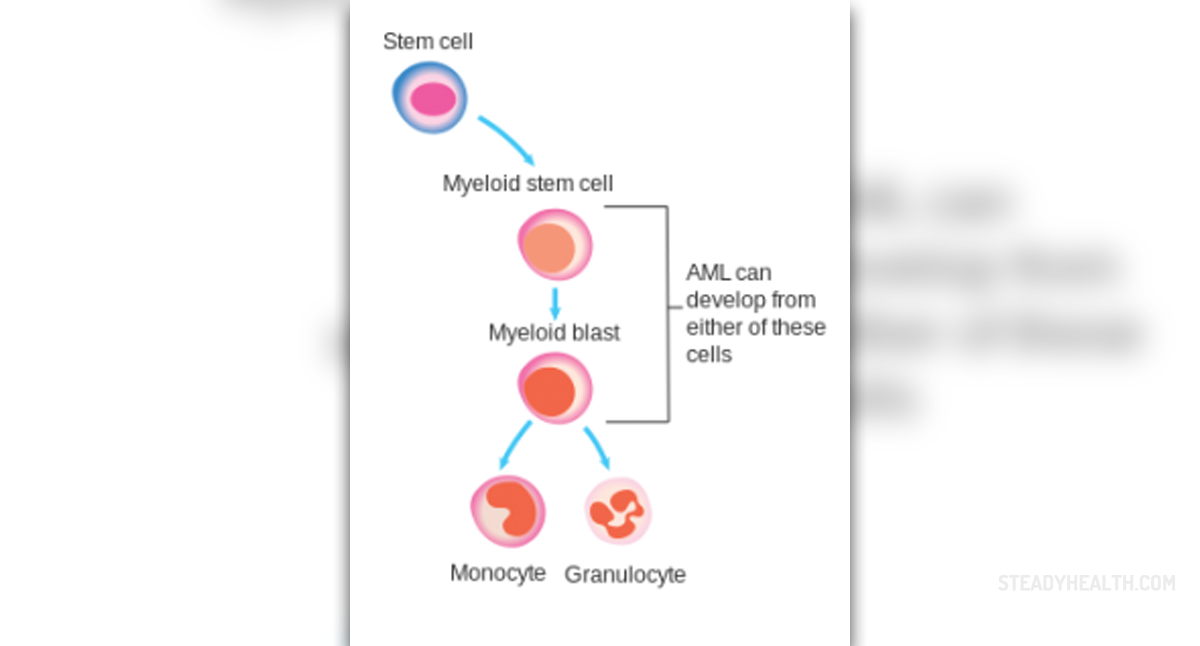
This particular type of leukemia is actually a cancer of the blood and the tissue in which the blood cells are created. This tissue is known as bone marrow and it is a part of the bones, or more precisely, it can be found within it. Due to the fact that myeloid cells, which are a group of white blood cells, are affected, this type of leukemia is called myologenous or myeloid. This disease progresses more than rapidly, and it might be really hard to notice it at its initial stage, because the symptoms that occur then are very similar to those of the flu. This is the reason why people usually do nothing about them, thinking that they will go away on their own. However, signs that will certainly indicate that something more than an ordinary flu is going on include easy bruising, unusual bleeding from the nose or gums, pain in the bones, tiredness and lethargy, and frequent infections.
Even though it is not really clear why the mutations in the DNA, which are responsible for this disease, occur in the first place, the experts believe that radiation, chemotherapy medications and certain chemicals might be some of the contributing factors. Those who are at higher risk are people who underwent chemotherapy or radiation therapy of any kind, people who are older than 65, and those with certain genetic and blood disorders. However, this is not a rule, because not everyone who is a part of the risk group will develop this type of leukemia.
Can it be treated and what options and methods are available?
As for the treatment, it differs depending on the stage of the disease, but it is a good thing to know that this disease can be cured in the majority of cases. However, whichever the stage, there are two parts of the treatment and the first, which is focused on destroying the leukemia cells in the blood and bone marrow, is called remission induction therapy. The second part of the treatment is called consolidation therapy or post-remission therapy, and it is focused on destroying the leukemia cells that have remained after the first part of the treatment. When the disease is discovered in the first stage, the treatment usually consists of chemotherapy, while the second phase of acute myeloid leukemia is treated with chemotherapy, although in some cases, a transplantation of the stem cells is also a part of the treatment. The third stage of this disease is most difficult to treat, and it definitely requires the transplantation of the stem cells.
- medlineplus.gov/acutemyeloidleukemia.html
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/acute-myeloid-leukaemia/
- Photo courtesy of Cancer Research UK by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Diagram_showing_the_cells_in_which_AML_starts_CRUK_297.svg













Your thoughts on this
Loading...