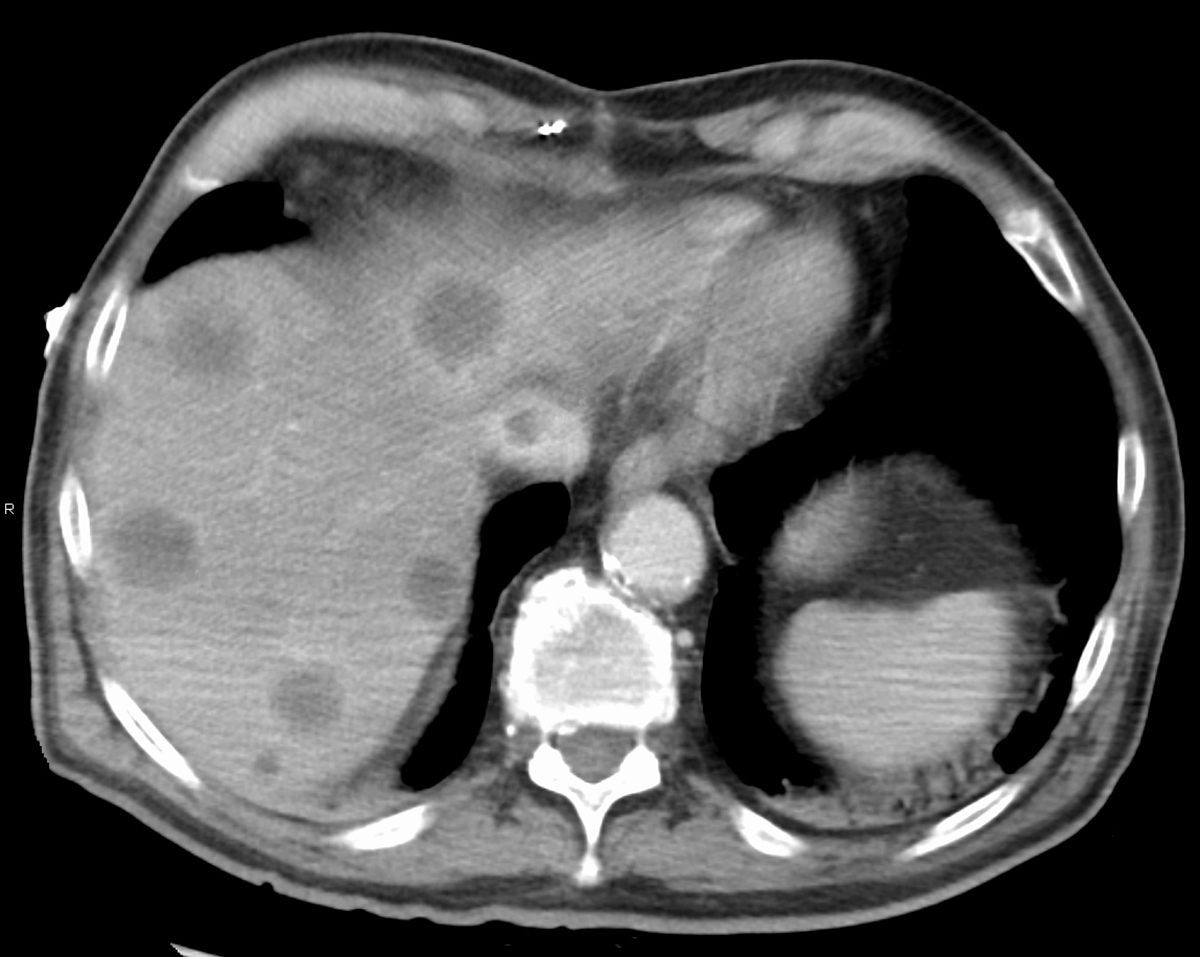
Budd-Chiari syndrome (hepatic vein obstruction) is a thrombotic or non-thrombotic blockage of the hepatic vein. There are two hepatic veins and their role is to drain de-oxygenated blood from the liver and blood cleaned by the liver into the inferior vena cava. The condition features with enlargement of the liver, ascites and abdominal pain and predominantly affects patients with underlying thrombotic diathesis (myeloprolipherative disorders, chronic inflammatory diseases etc.). What Causes Acute Budd-Chiari Syndrome?
The condition develops due to obstruction of the hepatic vein caused by a tumor or a growth pressing on the vessel from outside and it also occurs in case of blockage due to a blood clot which occurs in hepatic vein thrombosis. There are many medical conditions that can increase the incidence of clot formation and may be responsible for the onset of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Problems with coagulation are either inherited or acquired. They include myeloprolipherative disorders (polycytemia rubra vera, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria etc.), different cancers, chronic inflammatory diseases, autoimmune illnesses (systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren's syndrome etc.), infections, intake of oral contraceptives, pregnancy. And finally, in case the underlying cause simply cannot be identified Budd-Chiari syndrome is classified as idiopathic.
Clinical Characteristics of Acute Budd-Chiari Syndrome
Obstruction of the hepatic vein leads to congestive hepatopathy. This eventually leads to accumulation of the blood in the liver and its improper elimination. The final results are portal hypertension and liver insufficiency.
The condition features with a characteristic triad: abdominal pain, ascites (accumulation of fluid inside the peritoneal cavity) and hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver). Acute as well as subacute forms of Budd-Chiari syndrome include rapid development of all symptoms and signs. Apart from the previously mentioned patients also develop jaundice, splenomegaly (enlargement of the spleen) and may end up with renal failure. Excessive accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity leads to abdominal swelling and stretching.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Acute Budd-Chiari Syndrome
The condition can be diagnosed with the assistance of physical exam, laboratory findings as well as additional test and exams such as liver function tests, liver biopsy, ultrasound of the liver, Doppler ultrasound of the liver veins, CT scan or MRI of the abdomen. It is also essential to find the underlying cause or disease that has led to the onset of Budd-Chiari syndrome.
The goal of the treatment is to deal with the blockage, and restore normal flow through the hepatic vein. This can be achieved with several treatments which basically depend on the underlying cause of blockage. Some of them are administration of anticoagulation drugs, thrombolytic treatment, treatment for the liver-associated symptoms and signs etc. Surgical treatment for Budd-Chiari syndrome includes angioplasty and stent placement, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) and venous shunt surgery. If left untreated Budd-Chiari syndrome will progress into liver failure.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...