Enlarged Liver in Children
Children with enlarged liver or hepatomegaly usually have some underlying condition that has to be identified to choose proper treatment.
The liver is a vital organ in the body that performs a variety of functions. The liver is responsible for filtering the blood, making bile, processing fats, producing hormones that are involved in the clotting of blood, storing minerals and vitamins, and detoxification of the body. If the liver becomes enlarged, it can be a sign of certain diseases and this may occur in both children and adults.
Causes of Enlarged Liver in Children
Enlarged liver or hepatomegaly is not a disease but a sign of a disease. Several liver diseases may affect children and result in enlargement of the liver. Hepatomegaly is usually caused by viral infections of the liver. This may be hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C.

Chronic active hepatitis and neonatal hepatitis may also present enlarged liver as a symptom. Hepatomegaly may occur due to hepatoblastoma, which is a type of liver cancer mainly seen in newborns.
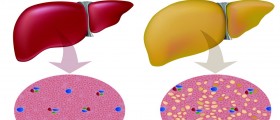
Accumulation of fat in the liver may be caused by Reye’s syndrome and result in an enlarged liver. Alagille syndrome features narrow and deteriorated bile ducts and leads to hepatomegaly as well.
Enlarged liver may be caused by inherited diseases such as Wilson’s disease, which causes the build-up of copper in the liver and galactosemia, which causes accumulation of sugars in the liver.
Other causes of hepatomegaly can be heart diseases, obesity, metabolic disorders, vitamins A and D toxicity, and prolonged use of certain medications.
When enlargement of the spleen follows enlargement of the liver, it is a condition known as hepatosplenomegaly. This condition is commonly caused by diseases that affect the kidneys, liver, or red blood cells.
- Weifang is in the central part of Shandong Province, where the inland and peninsulas of Shandong Province meet. It has a population of 10 million. The administrative area and population of Weifang rank second in Shandong Province. The incidence and epidemiologic trends of childhood liver disease in Weifang are representative of those of Shandong Province. Weifang People's Hospital is the largest tertiary first-class hospital in Weifang and a provincial-level regional medical center in Shandong. The hospital provides the highest level of pediatric medical care and diagnostic capacity in Weifang.
- A data that was analyzed is a retrospective study of clinical data from pediatric patients (age ?12 years) with liver damage in diagnosed at Weifang People's Hospital from June 2010 to May 2020.
- A total of 2632 children (1572 boys, 1060 girls) aged ?12 years were diagnosed with liver damage including infectious liver damage (2100 cases), non-infectious liver damage (446 cases) and liver damage of unknown etiology (86 cases). The most common causes of infectious liver damage were viral infection (1515 cases), Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection (343 cases), and bacterial infection (197 cases). The most common causes of viral liver damage were Epstein–Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and enterovirus.
- The most common causes of non-infectious liver damage were drug-induced liver damage, Kawasaki disease, and genetic metabolic diseases. There were 31 cases of severe liver damage.
Symptoms of Enlarged Liver in Children
When the liver in children is slightly enlarged, it may cause no signs and symptoms. But as the condition progresses and the liver continues to expand, the affected child may experience abdominal pain. The intensity of the pain depends on the severity of the condition. Enlarged liver is associated with yellowing of the skin and eyes, which is known as jaundice. Sometimes enlarged liver may present symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and lethargy. The liver may be tender to touch as well.
Treatment for Enlarged Liver in Children
Hepatomegaly can be identified by X-ray examination, ultrasound scan, CT scan, and blood tests. Treatment is determined depending on the underlying condition. In mild cases, children are prescribed drugs for treatment of the liver inflammation. In very severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...