Tracheotomy is a surgical procedure during which a doctor creates a hole in the trachea (the wind pipe) and inserts a tracheostomy tube. In order to reach the trachea the surgeon first makes a cut on the anterior aspect of the neck and this way reaches the organ. The tube inserted through the opening allows an individual to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. The procedure is generally performed if there is some obstruction in the upper respiratory tract which interferes in normal breathing. This is usually a temporary solution. Soon after the problem is dealt with and a person is ready to continue breathing by using the nose and/or mouth, the tube is removed from the trachea and the opening is closed.
Why is Tracheotomy Performed
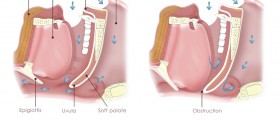
As it has already been mentioned tracheotomy is a form of bypass of the air which normally passes through the nose, mouth, pharynx and larynx but is because of some conditions temporary obstructed. The procedure is also performed in order to assist in removal of secretions from the airway. Via the tube oxygen can be directly administered into the lungs.
The following are some conditions which require prompt tracheotomy
foreign object in the throat that blocks the airwayadvanced cancer of the throat and neck which causes either obstruction or compression of the airwaysevere trauma to the mouth and/neck accompanied by intensive tissue swelling and closing of the airwayinhalation of irritants such as steam, smoke or come chemicalsunconscious state of mind that lasts for some time or a comaTracheotomy - the Very Procedure
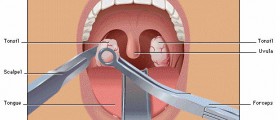
Under normal circumstances tracheotomy is performed in the operating room or intensive care unit. Prior the surgery patients are administered local anesthesia. A surgeon cuts open the neck and reaches the trachea paying attention not to damage any vital structures in the neck. Once the organ is opened, a tube is inserted into the trachea, just below the larynx.
Recovery after Tracheotomy
Patients recover soon after the procedure (after around 1-3 days). They may be uncomfortable initially, but they soon learn how to breathe through the tube. They also need to change their ways of communication. In the beginning it may be hard for patients to make sounds and talk. However, practice makes perfect and with proper training these functions are eventually restored. It is essential to learn how to take care of tracheostomy. For instance, when going out the opening should be covered with a lose scarf or other protective gear. Finally, special attention is paid to accidental exposure to food particles, water, aerosol etc.








-And-Breathing-Problems_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...