Cholinergic urticaria is a subtype of urticaria that features a sudden skin reaction. The condition occurs due to hypersensitivity to body heat. It typically develops after exercise, exposure to the sun, hot showers, and saunas, or it may develop after consuming spicy food. So all the previously mentioned stimulate the body to sweat and this consequently results in characteristic skin rash. To sum up, all the patients suffering from cholinergic urticaria develop symptoms of the disease after they are exposed to any kind of stimuli that induce increased production of sweat.
Pathophysiology and Causes of Cholinergic Urticaria
The hypothalamus is the part of the brain in charge of the regulation of body temperature. Once it detects an increase in the body temperature it signals the sweat glands to produce sweat. This is achieved thanks to a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. This neurotransmitter assists in the degranulation of specific cells in the skin called the mast cells. The mast cells disintegrate and release histamine. Since plenty of mast cells release excessive amounts of histamine rapidly this consequently activates the inflammatory response of the nearby tissues.
The very inflammation is in the form of skin flushing, and the skin becomes sticky and prickly. Normally, a release of sweat from the sweat glands ceases the hypersensitive reaction. But, in people suffering from cholinergic urticaria, it is hard to release sweat, and this leads to specific symptoms and signs of the disease.
Symptoms of Cholinergic Urticaria
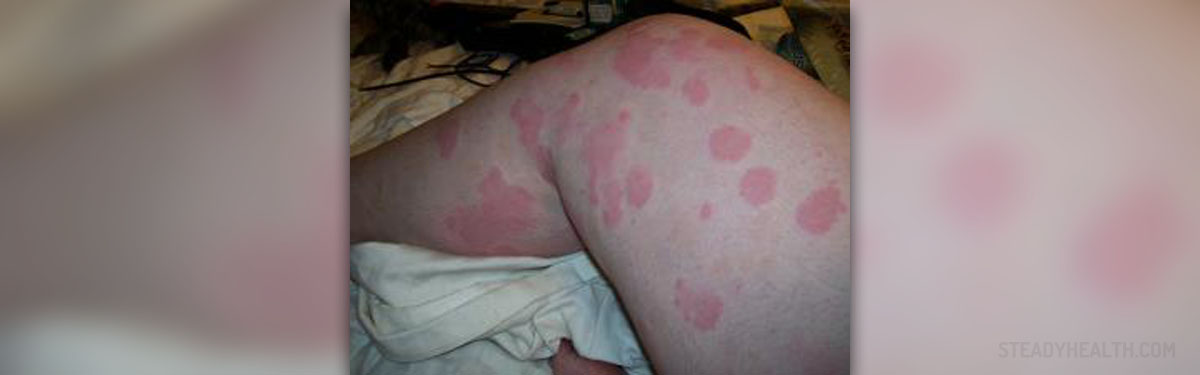
People suffering from cholinergic urticaria start to experience unpleasant sensations the moment the temperature of the surroundings starts to increase. The skin becomes extremely itchy, and this sensation may affect every part of the body. Still, the itching sensation most commonly affects the face, scalp, and upper torso. The person may also complain about prickling and tingling sensations.
One more characteristic of cholinergic urticaria is flushing or reddening of the skin. Reddening of the skin occurs due to dilatation of the skin's blood vessels. In some cases, the skin is covered with small, pinpoint hives. Furthermore, skin changes may be in the form of small weals and raised welts, but they only occur if the skin is vigorously scratched. And finally, there is generalized anhidrosis. A lack of sweat production is either partial or total.
Treatment for Cholinergic Urticaria
This type of urticaria is rather challenging to treat. A patient needs to identify potential triggers and avoid them. Since many people may feel the attack of urticaria coming on they may try rapid cooling and apply cold water or ice pack onto the skin. The doctors most commonly prescribe antihistamines. These medications are effective and may prevent outbreaks of cholinergic urticaria. Corticosteroids are prescribed only in the severe form of the disease.
- Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody specifically designed to simultaneously inhibit the activity of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13), which play a key role in the inflammation cascade of type 2.
- We report the case of a 26-year-old man suffering from CholU for 3 years, unresponsive to standard treatment in which off-label therapy was undertaken with Dupilumab, 600 mg subcutaneous as a loading dose and then 300 mg every 15 days.
- The daily Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score was used to assess the efficacy of the therapy. Already after the first two administrations, the patient no longer had CholU episodes and resumed regular sporting activity, with a marked improvement in the quality of life.
- A possible mechanism of Dupilumab in reducing the manifestations of CholU is the blocking of the IL-4 pathway and the expression of the high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc?R1) on B cells, mast cells (MCs) and basophils. By decreasing the production of Fc?R1, the adhesion of IgE to the surface of MCs decreases with consequent reduction of MCs activation and histamine release.


-Causes,-Symptoms-And-Diagnosis_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...