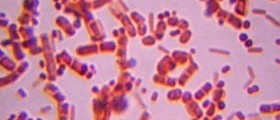
Bubonic plague is an infectious disease that is primarily transmitted by the bite of the infected fleas. The fleas transfer the infection from rodents to humans. The actual culprit of bubonic plague is a bacterium called Yersinia pestis. The bacterium may in extreme cases be transferred from one person to another.
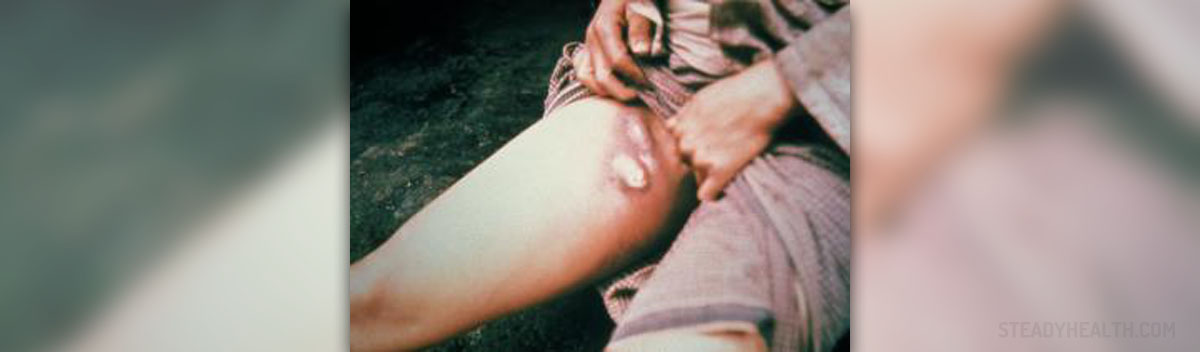
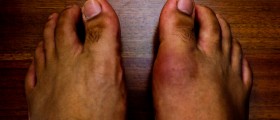
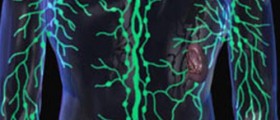
Lymph nodes (especially those in the armpits and groin area) are in patients suffering from bubonic plague enlarged and swollen. In case the infection is not treated it may cause lethal outcome in only 2-6 days.
The bacteria responsible for bubonic plague is found in infected rodents. In case the fleas from the infected rodents come in contact with humans they may transfer the bacterium with a single bite. The bacterium enters the lymphatic system and starts to multiply within the lymph nodes. Hence the enlargement of lymph glands.
Presentation of Bubonic Plague
The first symptoms and signs of the infection develop 2-5 days after a person has been exposed to the bacteria.
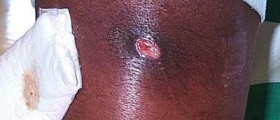
The leading sign of bubonic plague is a so called bubo, an enlarged lymph node. Swollen lymph nodes are painful. The bacterium most commonly affects the lymph nodes in the armpits, groin or neck. Apart from swelling of the lymph nodes a patient suffering from bubonic plague also develops chills and a high fever (102 degrees F). He/ she is weak, complains about the muscle pain and a severe headache. In some cases there is a possibility of seizures.
More severe symptoms and signs of the infection include heavy breathing and coughing, continuous blood vomiting, urination of blood and aching limbs.
If the infection is not treated the buboes start to decay and decompose and this is accompanied by severe and unbearable pain. The terminal stage of the disease features with extreme tiredness, gastrointestinal problems and formation of lenticulae, black dots that are scattered and affect the entire body. The person eventually develops delirium and enters a coma.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Bubonic Plague
The doctor evaluates the patient's medical history and performs physical examination. In case he/ she suspects that a person is suffering from bubonic plague the patient will undergo additional test and examinations. Definitive confirmation of the infection is obtained by identification of Yersinia pestis culture (samples are taken from the patient).
Patients suffering from bubonic plague are hospitalized and put in isolation. Even before conformation of the infection patients are administered potent antibiotics. There is also a need for supportive care. There are several antibiotics highly effective against bubonic plague and they include streptomycin and gentamicin, tetracyclines and fluoroquinolone Ciprofloxacin.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...