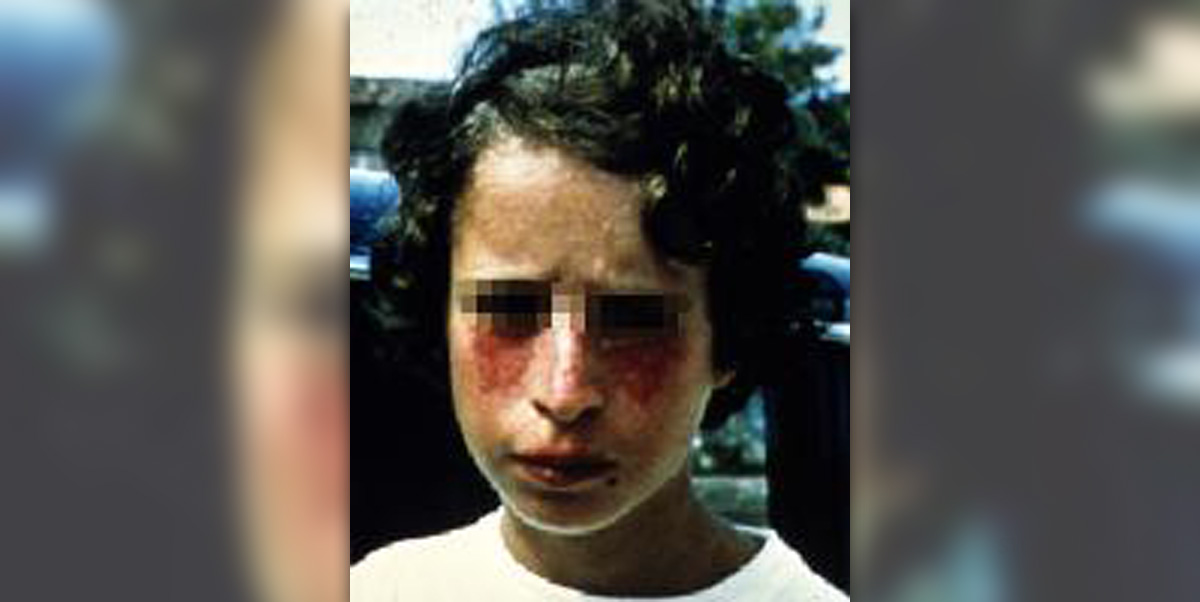
Bloom-Torre-Machacek syndrome or simply Bloom’s syndrome is a certain rare medical condition which is classified as an autosomal recessive chromosomal one. The person affected by this medical condition suffers from frequent breaks and rearrangements of chromosomes.
Causes
The DNA helicase family contains a BLM gene, the one which triggers the Bloom’s syndrome once it gets mutated. These helicases are actually certain types of enzymes whose main purpose is to unwind the strands of DNA molecule. The unwinding is a rather necessary process for DNA repair, RNA transcription, synthesis of DNA copies and various other processes. The chromosomes get duplicated each time a new cell prepares to be divided in order to form two new cells. This process is medically referred to as DNA replication and when certain errors occur while it takes place, it all leads to the occurrence of mutations. The Bloom’s syndrome is commonly associated with an extreme increase in exchange events between sister chromatids and chromosome rearrangements and breakage. It is not yet fully understood what causes these harmful processes on such levels, though it is a scientifically established fact that Bloom’s syndrome is a medical condition characterized by an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. This means that the disorder can be inherited, but only in cases when both parents carry the syndrome. There are also certain other types of mutations which may occur and trigger the Bloom’s syndrome. The enzyme called pyruvate kinase may sometimes develop certain missense mutations which are scientifically referred to as K422R and H391Y.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of the Bloom’s syndrome include a facial rash which occurs rather shortly after exposure to sun and a characteristic short stature of a person. It is also very common for the aforementioned rush to form a patch of reddened skin in the form of a butterfly on the cheeks. The rash may sometimes develop on certain areas of the skin which are not exposed to sunlight.
Other possible symptoms of this dreadful medical condition may or may not include premature menopause, premature cessation of menses, failure to produce sperm, hypogonadism, ear infections, recurrent pneumonia, deficiency in certain immunoglobulin classes, moderate immune deficiency, dilated blood vessels, café-au-lait spots, hyperpigmented areas, hypopigmented areas of the skin, narrow and long face and high pitched voice.
Women who suffer from the Bloom’s syndrome may still have children in some cases. The big problem with the Bloom’s syndrome is that it may also be involved with a large number of further medical complications and these basically include mental retardation, learning dis abilities, diabetes and chronic lung problems. Bloom’s syndrome is additionally known for being closely related to certain types of cancer such as carcinomas, lymphomas and leukemia, among others.
Statistics
According to certain statistical data, there are approximately 6,117 cases of Bloom’s syndrome in the United States alone. Based on such facts the statistics has led to the conclusion that there are also approximately 677 cases of Bloom’s syndrome in Canada and 2,186 cases in Mexico.
As far as Central America goes, there have been 5 cases of Bloom’s syndrome in Belize, 297 in Guatemala and 111 cases in Nicaragua.
As far as the Caribbean goes, there have been 81 cases of Bloom’s syndrome reported in Puerto Rico. Bloom’s syndrome in South America included 3,835 cases in Brazil, 329 cases in Chile, 881 cases in Colombia, 128 cases in Paraguay, 573 cases in Peru and 521 cases in Venezuela.
Bloom’s syndrome in Northern Europe included 112 cases in Denmark, 108 cases in Finland and 187 cases in Sweden. As far as Western Europe goes, there have been 1,255 cases of Bloom’s Syndrome in the United Kingdom, 215 cases in Belgium, 1,258 cases in France, 82 cases in Ireland, 9 cases in Luxembourg, 339 cases in Netherlands and 60 cases in Wales. Bloom’s syndrome in Central Europe has included 170 cases in Austria, 25 cases in Czech Republic, 1,717 cases in Germany, 209 cases in Hungary, 804 cases in Poland, 112 cases in Slovakia, 41 cases in Slovenia and 155 cases inSwitzerland. As far as Eastern Europe goes there have been 214 cases of Bloom’s syndrome in Belarus, 27 cases in Estonia, 48 cases in Latvia, 75 cases in Lithuania, 2,999 cases of Russia and 994 cases in Ukraine. Bloom’s syndrome in Southwestern Europe has included 163 cases in Azerbaijan, 97 cases in Georgia, 219 cases in Portugal and 839 cases in Spain. As far as Southern Europe goes, there have been 221 cases of Bloom’s syndrome in Greece and 1,209 cases in Italy. Bloom’s Syndrome in Southeastern Europe has included 73 cases in Albania, 8 cases in Bosnia and Herzegovina, 156 cases in Bulgaria, 93 cases in Croatia, 42 cases in Macedonia, 465 cases in Romania and 225 cases in Serbia and Montenegro.
There have also been 57 cases of Bloom’s syndrome in Mongolia, 315 cases in Kazakhstan, 146 cases in Tajikistan, 550 cases in Uzbekistan, 27,059 cases in China, 142 cases in Hong Kong, 2,652 cases in Japan, 9 cases in Macau, 472 cases in North Korea, 1,004 cases in South Korea, 473 cases in Taiwan, 1,435 cases in Turkey, 594 cases in Afghanistan, 2,994 cases in Bangladesh, 45 cases in Bhutan, 22,188 cases in India, 3,316 cases in Pakistan, 414 cases in Sri Lanka, 21 cases in East Timor, 4,967 cases in Indonesia, 126 cases in Laos, 490 cases in Malaysia, 1,796 cases in Philippines, 90 cases in Singapore, 1,351 cases in Thailand, 1,722 cases in Vietnam, 27 cases in Gaza Strip, 1,406 cases in Iran, 528 cases in Iraq, 129 cases in Israel, 116 cases in Jordan, 47 cases in Kuwait, 78 cases in Lebanon, 537 cases in Saudi Arabia, 375 cases in Syria, 52 cases in United Arab Emirates, 417 cases in Yemen, 1,585 cases in Egypt, 48 cases in West Bank, 117 cases in Lybia, 815 cases in Sudan, 62 cases in Congo, 432 cases in Ghana, 70 cases in Liberia, 236 cases in Niger, 369 cases in Nigeria, 226 cases in Senegal, 414 cases in Australia and 83 cases in New Zealand.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...