
CIDP is a short name for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, an acquired immune-mediated inflammatory disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. The acute version of this disease is known under the name Guillain–Barré syndrome. Guillain–Barré syndrome, or short GBS, is an acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (or AIDP), a disorder that severely affects peripheral nervous system and may even cause life-threatening complications. This is a rare disease that affects one or two per 100,000 individuals yearly, and yet it remains one of the leading causes of acute non-trauma-related paralysis worldwide. GBS is also known as acute idiopathic polyradiculoneuritis, acute idiopathic polyneuritis, French polio, Landry's ascending paralysis and Landry Guillain Barré syndrome.
Signs and symptoms of acute CIDP
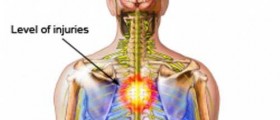
Guillain–Barré syndrome usually manifests as ascending paralysis. The patients first notice weakness beginning in the feet and hands, but very soon these symptoms will start spreading towards the trunk. The weakness is usually symmetrical and first affects the lower limbs. The legs may feel rubbery and tend to buckle, but the disease rapidly progresses upwards, affecting the rest of the body. Sometimes, the arms and facial muscles may become affected in just a couple of hours after the initial symptoms appear. Most patients will require hospitalization in up to a couple of days and about one third will require ventilator assistance.
Prominent symptoms include facial weakness, bulbar weakness, drooling, difficulty swallowing and respiratory difficulties. Patients may also experience sensory loss, loss of deep tendon reflexes, as well as loss of pain and temperature sensation. In severe cases, Guillain–Barré syndrome is also associated with fluctuations in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Causes of acute CIDP
Guillain–Barré syndrome is caused by immune response to foreign antigens. Actually, in this disease, human body mistargets the host nerve tissues instead of the foreign antigens and attacks gangliosides, compounds naturally present in large quantities in human nerve tissues. Scientists believe that most commonly, our immune system reacts in such a way following the infection by Campylobacter jejuni. However, for more than 60% of all cases, the causes are unknown.
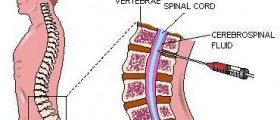
When the immune system attacks peripheral nerves, it damages myelin, a protective layer around the nerve. This leads to muscle paralysis and sensory or autonomic disturbances. In mild cases, the nerves can repair if remyelination occurs. However, in severe cases, nerves may be seriously damaged. To some extent, this condition is similar to multiple sclerosis and Lou Gehring’s disease, but unlike these diseases it doesn't cause nerve damage to the brain and spinal cord.
In most cases, recovery starts after a month from the onset of disorder. About 80% of patients completely recover within a couple of months. Only about 5–10% patients recover with severe disability







-and-Multiple-Sclerosis-Differences-And-Similarities_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...