
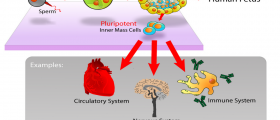
First of all you should know about stem cells. Stem cells are the cells which may become any of other cells in the body. Because of that fact, there is a potential in using these cells to repair damaged organs and tissues. Scientists hope that the development of stem cells will enable them to cure Parkinson’s disease, heart problems, diabetes, or even Alzheimer’s disease. There are three types of stem cells: embryonic, fetal and adult stem cells. All of these can be found in both humans and animals.
Fetal Stem Cells
Fetus is a human embryo after 8th week of development. Fetal stem cells are present in the umbilical cord blood, the placenta and aborted fetuses. There are some people that decide to donate these cells after the birth of their child or decide to preserve those cells in case the child needs them later in life. Many of the fetal cells are already differentiated into certain body cells. However, some still obtain the possibility to be transformed into all body cells. Fetal cells are proven to be helpful in treating leukemia in children, but the disease could come back and might not be easily treated. So, fetal cells do have advantages and fails. They are more successful than bone marrow transplant and provide a better match in transplanting among minorities, but the problems of transmitting diseases through fetal stem cells still remains.Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are produced from fertilized eggs (embryos). 5 days after the fertilization egg cells start to change (differentiate) and form two masses, that will become placenta and fetus. Embryonic stem cells (those that should become fetus) are isolated and used for research.These stem cells can be grown into any cells of the body: skin, brain, organs, etc. The process of growing them into particular organ or tissue and stopping their growth once they develop into wanted organ still represents a challenge for the scientists. Further development is a problem since the overgrowth of the cells may become a tumor. Another problem is the rejection of grown organ or tissue by the recipient patient. Possible solution is a process known as “therapeutic cloning”. Patients own cells are placed into the unfertilized egg and then the fertilized, providing higher genetic match and lesser risk of transplant rejection. This is not the same as “reproductive cloning”, which is still illegal in most countries of the world, while the therapeutic cloning research are legal.Adult Stem Cells
They are present in the human body in both children and adults, but are hard to be identified and isolated. Usually, doctors take adult bone marrow stem cells and use them in cancer therapy. The only problem is that in 100.000 of bone marrow cells there is just one stem cell. There are clinical trials ongoing that research the use of these adult stem cells in the heart diseases. Some adult stem cells are predefined to become certain cells. However, lab testing on animals reveals that these stem cells can also be differentiated into variety of different body cells. There are small risks that transplanted organ made of stem cells will be rejected, since the patient can be transplanted with his/hers own adult stem cells.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...