Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Borrelia. Depending on the part of the world, different species of bacteria belonging to this genus are main cause of the disease. For example, Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii cause most European cases, while their relative Borrelia burgdorferi sensu strict, causes the most cases in the United States. The disease was first identified in the town of Lyme, Connecticut, USA, in mid 70’s. However, it was not before 1981, that scientists discovered what exactly causes the disease.
Causes of Lyme disease
Lyme disease is a tick-borne disease, which means that it is transmitted by ticks. People are becoming infected by borrelia by the bite of infected ticks belonging to a few species of the genus Ixodes. Ixodes are hard-bodied ticks known to transmit the pathogenic bacteria such as Borrelia, Babesia, Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. The Borrelia species that cause Lyme disease are collectively known as Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. The bacteria are transmitted to humans by thick bites that often go unnoticed. However, this is a rare disease and only around 1% of recognized tick bites resulting in Lyme disease. It is estimated that an infected thick must remain attached to the skin for at least a day for transmission to occur.
Symptoms of Lyme disease
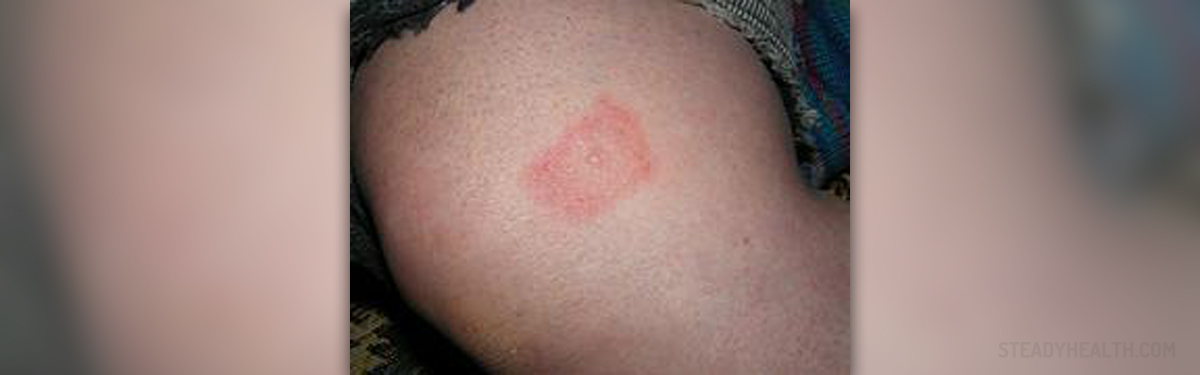
Lyme disease can produce a wide range of symptoms. Most of the patients won’t have all of the symptoms but in some severe cases, even multiple body systems can become affected. In general, it takes about two weeks before patients start feeling the symptoms. First sign of the infection is small local infection that occurs at the site of the original bite. The rash is usually red, warm, with dark red innermost portion and red outer edge. The portion between is typically clear, and the rash has a characteristic “bulls eye” appearance. Some patients can also experience flu-like symptoms at this stage. Early disseminated infection occurs within a couple of days or weeks after the onset of local infection, when the bacteria start spreading through the bloodstream. Patients usually complain about pain in muscles, joint, and tendons, and heart palpitations and dizziness in this stage. In Europe, patients may also develop a purple lump on the ear lobe, nipple, or scrotum. If the condition is not treated it occasionally causes chronic neurologic symptoms such as hooting pains, numbness, and tingling in the hands or feet. Other problems such as depression, fibromyalgia, vertigo, bladder problems, and even schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, are also observed.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...