Introduction
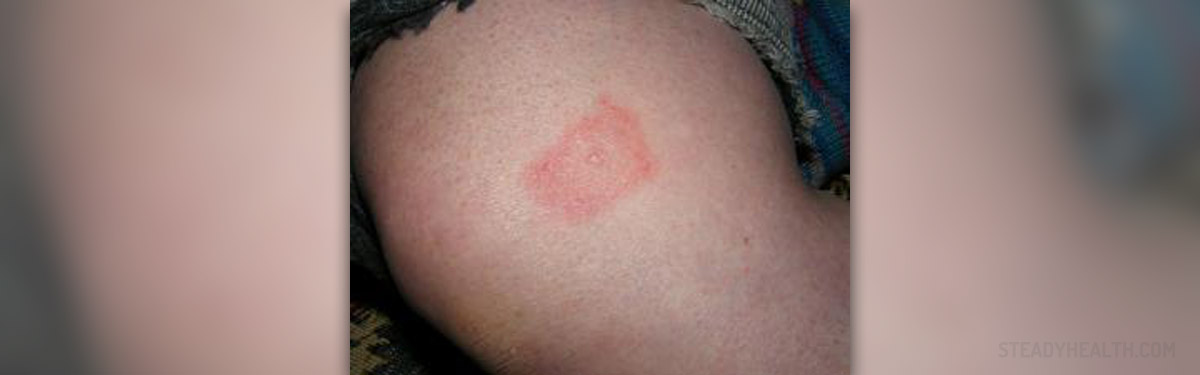
Ixodes scapularis tick, or more commonly known as a deer tick or blacklegged tick, is an insect that can carry the Borrelia burgodrferi which causes the lyme disease. Borrelia burgodrferi is a spirochete, microscopic bacterial organism that is coated with protein-like membrane. These proteins allow the B. burgodrferi to stick to the human cells and cause the health problems referred to as the lyme disease. The infection is spread only by Ixodes scapularis tick containing B.burgodrferi, mainly found in the regions of the northeast or central United States. The tick causes the lyme disease, babesiosis and human granulocytic anaplasmosis which is very rare. The percentage of people affected with two of these diseases is very low.
The tick first gets the spirochete through sucking the blood of the mouse that carries it. The tick is still a larva so the blood helps it to grow. Then, the tick can be said to carry B.burgodrferi which places itself in the tick in the 2nd and 3rd stage of the tick's life cycle, The tick can thus transmit the spirochete to the humans or animals. The mature ticks are most commonly found in June and when they attach themselves to the human they are not easily seen. They can be seen though after sucking the blood and after a few days they fall off the skin. There is enough time for them to pass the spirochete into the body. The infected human cannot transmit the lyme disease to the other one.
Treatment
Lyme disease can be treated with antibiotics when it is diagnosed in the initial stages. On the other hand, if the treatment does not start as soon as possible, people who have been bitten by a tick can continue to have health complications. Even at later stages, antibiotics may help ease the symptoms of the lyme disease. However, untreated lyme disease leads to serious health problems affecting any organ. Most frequently, it provokes the inflammation of the joints so a person can have swollen and painful joints on legs or arms. Tingling sensations all over the extremities or their weakness are felt a long time after the tick's bite. Other complications include the mental and emotional problems too. The person is likely to feel depressed and very weak, unable to concentrate and think properly. If the disease affects the heart, the heart rate decreases.
The lyme disease is effectively cured by the antibiotics. There are very rare cases of people who experience some problems after having cured the lyme disease. This is called post-lyme disease syndrome, whose symptoms fade away after some time.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...