Anticonvulsant Drug Therapy For Epilepsy Seizures
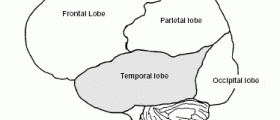
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurring seizures. When the neurons in the brain start firing signals uncontrollably or faster than normal a seizure is likely to occur. In most cases, seizures are kept in check using anticonvulsant medications. Depending on the patient’s age, other underlying or acute illnesses, as well as the intensity and frequency of seizures, a medical care professional prescribes the proper medications. Another very important aspect in choosing the right treatment involves an adequate diagnosis, which is usually achieved using an MRI scan. When it comes to different types of medications, there is a wide range to choose from, including some older and some newer types. The more standard or traditional medications include tranquilizers, such as Valium, Depakene, Zarontin, Carbatrol, Dilantin and Phenobarbital. Some of the newer drugs are Trileptal, Neurotonin, Keppra, Felbatol, and Gabitril. Most of these drugs will be adequate for treating different types of epilepsy. The kind that the doctor will prescribe will likely depend on other included elements, such as the side effects, the patient’s proneness to allergies, or the presence of another chronic illness or disorder. It should be noted that anticonvulsant medications are effective in about 70 percent of the cases. Also, drugs do not provide a cure, but rather a relief from the symptoms, and it usually takes a long time to discover the right dose in order to minimize both the seizures and the side effects produced by medications. It is very difficult for a health care provider to determine in advance the types and extent of side effects the individual will experience. As a result, the doctors usually start will a low dosage and monitor the blood levels for the effects of the medication to assess the optimal dosage. In most cases the severity of the side effects determine the type of anticonvulsant drug the patient will be using. In many instances a combination of different kinds of treatments, such as medications and surgery, prove to be the most effective. Lastly, the possibility that a person will eventually be able to stop taking the medication depends on different factors, but it definitely does exist. Children who are diagnosed in early stges and had been under medical care for a long time have a chance to stop taking the drugs in adulthood without experiencing any more seizures.Surgery For Epileptic Seizures
In cases in which more than 2 or 3 different types of medications are not effective in a period of about 2 years it is recommended that the patient undergoes surgery. Out of the 30 percent of individuals who are not responding well to medications only about one third qualify for surgery, which equals about 100, 000 persons in the US. Every year, there are approximately 3,000 epileptic surgeries performed in America. Before the decision is made to perform the surgery a presurgical exam will be administered for the purposes of assessing the outcome of the intervention. If it is decided that no damage will be done to any essential functions in the brain while at the same time reducing the frequency and intensity of the seizures the patient will be considered a good candidate for the operation. The assessment is composed of EEG video monitoring and other related exams to try and locate the area where the seizures are occurring. The exact site of the seizures as well as the damaged cells in the brain determine whether the surgery can be successful as well as the technique which should be used. A team of specialists, including a neuropsychologist, epileptologist, neurosurgeon, neuroradiologist and a social worker, assesses the potential risks and benefits of surgery. If the patient is suffering from partial epilepsy he or she is more likely to be considered for surgery, as there is only one area of the brain involved in the seizures. In most cases the surgery frees the patient of seizures, while in others it reduces their frequency and intensity. In a few instances more than one operation is required to reach favorable results.Other Treatment Options
Medical care professionals will often recommend a special king of diet called ketogenic diet. The ketogenic diet has been gaining in popularity lately, and it has primarily been prescribed to children who are not responding well to medications. As the diet is fairly complicated to follow it usually starts in a clinical setting and is retained for about 2 to 3 years. In addition, there has been a new kind of treatment used to help decrease the seizures and it involves surgically placing a little stimulator in the upper chest area. The stimulator seems to be effective in reducing the number of seizures when the medications do not produce the desired effects. The stimulator decreases the number of seizures in approximately 40 to 50 percent of patients by a half, but is not expected to eliminate them completely. The stimulator is usually combined with anticonvulsant drugs to deepen its effect.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...