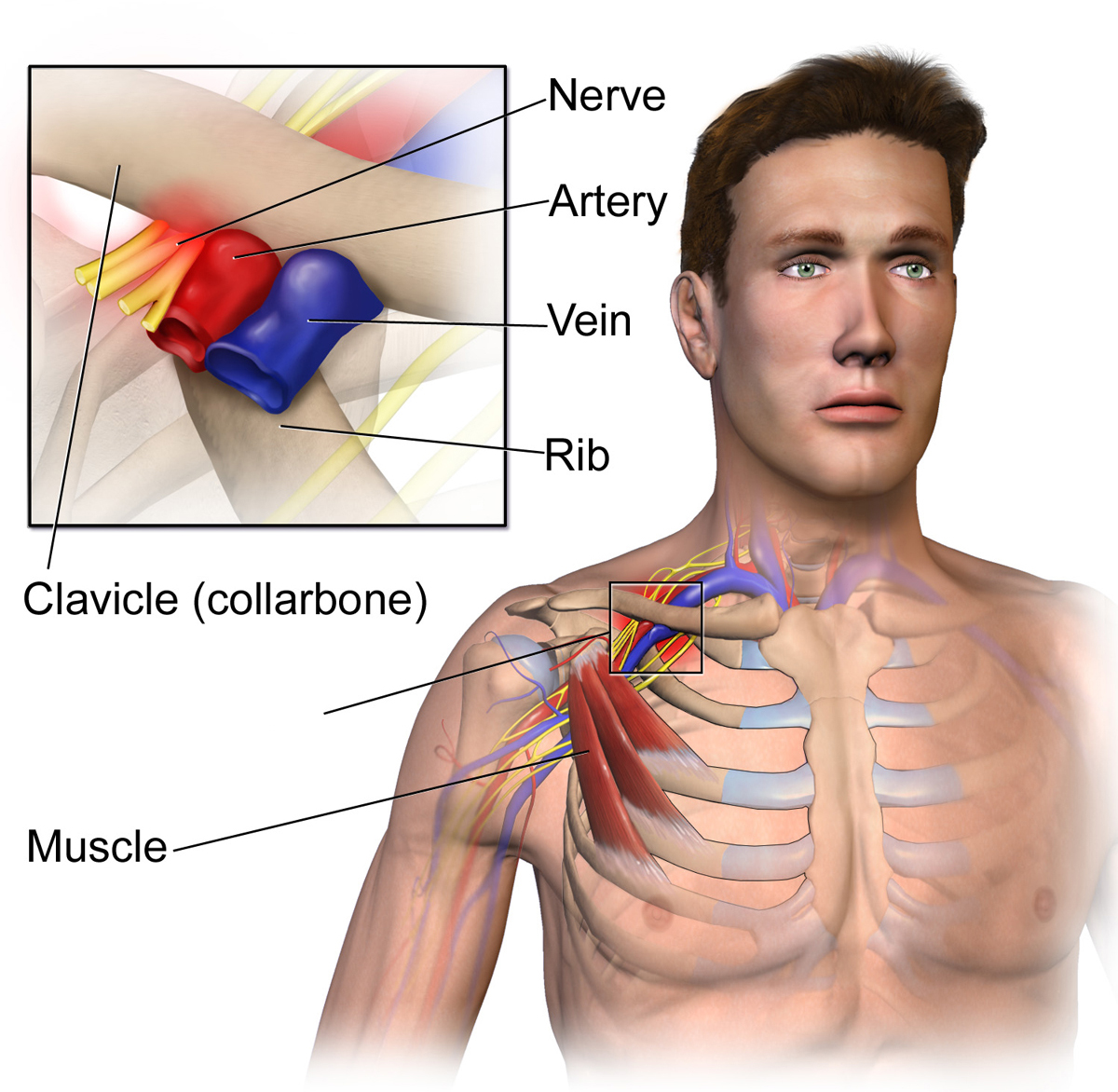
Thoracic outlet is an area between the clavicle and the first rib. Thoracic syndrome is a medical condition which develops due to compression of blood vessels or nerves in the thoracic outlet. Compression of the mentioned structures leads to pain in the shoulders and the neck and numbness of fingers. The most common cause of thoracic outlet syndrome is physical trauma caused by a car accident. It also affects people exposed to repetitive injuries related to professional or sports activities. In some cases, the underlying cause of thoracic outlet syndrome simply cannot be identified. Thoracic outlet syndrome can be classified into neurological, vascular and non-specific type. In neurological type the compression affects the brachial plexus, in vascular type certain blood vessels are compressed while in non-specific type the exact cause of the syndrome cannot be identified.
Symptoms of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Symptoms of this disorder vary a lot since numerous structures may be compressed. In case of nerve compression patients commonly complain about shoulder pain, neck pain, ache in the arms or hands and numbness or tingling sensation in fingers. The grip is usually weak. Compression of blood vessels leads to bluish discoloration of the hand, subclavian vein thrombosis, arm pain and arm swelling. The doctor may palpate throbbing lump near the collarbone. Fingers or entire hand may be pale and in extreme cases fingers are covered in tiny black spots which represent infarcts of the finger blood vessels.Causes of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Compression of certain structures may be caused by:a variety of congenital or acquired anatomical defects (a cervical rib)poor posture (drooping of shoulders )trauma (car accidents etc.)repetitive activity (a variety of sports activities)pressure on specific joints (obesity)pregnancy (loosening of the joints)Treatment for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
The basic concept of treatment is related to reduction of pain. Majority of patients are treated conservatively. This treatment modality includes physical therapy, medications and relaxation. Surgery is performed only if thoracic outlet syndrome symptoms do not respond to conservative therapy. Surgery is the only effective treatment modality in patients suffering from neurological thoracic outlet syndrome. Surgery only takes care of the cause. It does not improve the strength of the affected muscles. Two most frequently performed surgical procedures are anterior supraclavicular approach and transaxillary approach.
Physical therapy is basically performed at home after the patients have had consultations with physical therapist and have been explained exercises they are supposed to do. The goal of physical therapy in thoracic outlet syndrome is strengthening of the affected muscles. Additional measures include maintaining of the good posture and practicing relaxation techniques.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...