
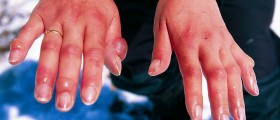
All people must be familiar with actions they are bound to take if someone from their surrounding suffers from burns.
Before the very treatment begins the person who is close to a casualty is due to stop the burning process, then asses the airway, breathing and circulation of a casualty, evaluate the extent as well as the depth of the burn, assess the criteria for consulting a burn center and finally estimate whether there are associated injuries.
Treatment for Burns
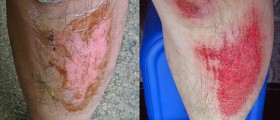
Mild burns are treated at home and they sometimes need medical attention. Severe burns, on the other hand, affect large potions of the skin, are deep and life-threatening due to mechanisms initiated by the loss of fluid.
This is why fluid replacement represents a cornerstone of initial burn treatment. After the area is burnt, damaged capillaries start to leak. This leads to huge fluid loss. In case of large burns the fluid may accumulate anywhere inside the body. Furthermore, the one loses fluid through unprotected tissues (parts affected by burns which are no longer covered with the skin). So with optimal fluid replacement we can prevent hypovolemic shock and all the associated complications.
Fluid Resuscitation
Depending on the extent of injury and several more factors, fluid resuscitation can be achieved with oral fluids and more complex cases require intravenous administration of fluids.
There are different formulas used for optimal fluid resuscitation. They are quite efficient in maintaining the volume during the critical period of hypovolemia. For instance, some burning centers use the Parkland Formula. It provides with optimal fluid resuscitation and is quite easy to remember. In order to evaluate the effects of fluid resuscitation doctors monitor patient's urine output.
Some Complications
Patients with electrical injuries may suffer deep tissue damage and this is responsible for the presence of large amounts of myoglobin in their urine. Their urine output must be doubled in order to eliminate large myoglobin molecules.
Fluid resuscitation can be a trigger for edema. Namely, major burns of an extremity of the torso are prone to swelling. The skin becomes quite rigid and does not allow expansion. As a result such tightness may compromise circulation and cause different complications like loss of peripheral pulses or loss of motor or nerve function. The affected extremity may even become cyanotic. This is why people with the mentioned burns require thorough monitoring especially when it comes to tightness of the extremities, loss of pulses and complaints such as numbness or tingling.
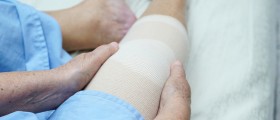
Finally, once the condition is brought under control, doctors can plan further steps of burn treatment such as skin transplants and reconstructive procedures.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...