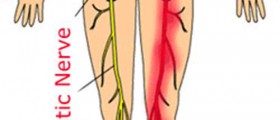
Radial nerve palsy is a type of mononeuropathy affecting the radial nerve. The condition is also known under the names wrist drop deformity or just wrist drop. The radial nerve is located in the arm and represents the largest nerve of the brachial plexus, a bunch of nerves predominantly innervating the upper extremity. The nerve starts at the base of the neck and spreads to the lateral epicondyle where is separates into two branches, one traveling to the skin of the back of the hand and the other reaching the extensor muscles lying beneath this portion of the skin.
Radial Nerve Palsy Clinical Characteristics
Typical symptoms affecting patients suffering from radial nerve palsy include loss of sensation in the area innervated by the nerve, immobility (the person finds it difficult to use the affected arm, extend or bend the affected arm), tingling or burning sensation and sometimes pain. If radial nerve palsy lasts for a long period of time, fingers may turn pale in color.

- Radial nerve palsies in closed humeral shaft fractures are common, with an incidence of 7%-17%.
- The management of radial nerve palsies in closed fractures is often expectant, with 70.7% spontaneously recovering within six months.
- A literature search was conducted for studies on radial nerve palsies in humeral shaft fractures from 2000-2018. A total of 4972 humeral shaft fractures were identified, with an incidence of 12.2% of primary radial nerve palsies.
- During the exploration, no neurological intervention was performed in nearly 41% of cases, and the most common finding was no evidence of any nerve lesion (35%).
Radial Nerve Palsy Medical Therapy
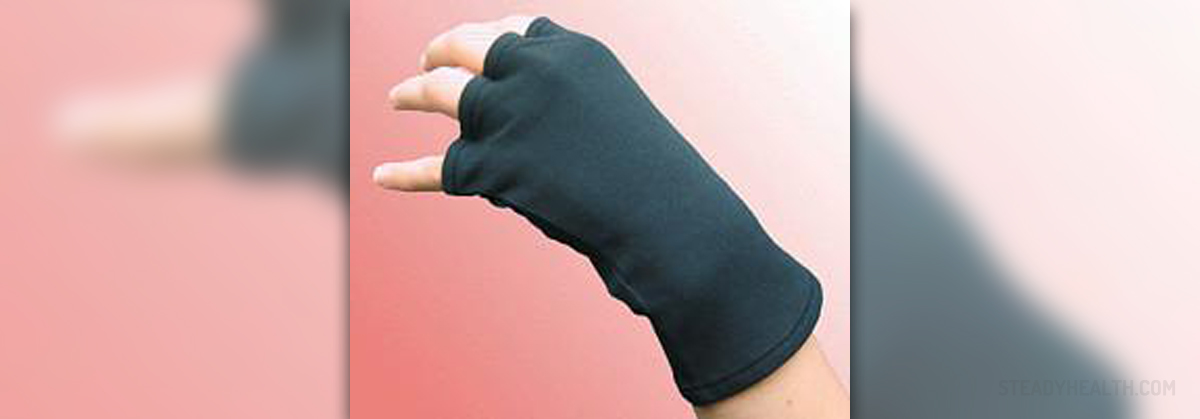
Conservative treatment for radial nerve damage or palsy depends on the severity of the condition. Swelling of the nerve can be significantly reduced with adequate immobilization and anti-inflammatory drugs. Additional help is obtained from functional splints which prevent contracture and may assist in improving functions that have been lost. So splints and activity modification represent the most significant treatment modalities when it comes to radial nerve disorders.
If there is compression of the superficial radial sensory nerve, the one benefits most if the underlying cause of compression is brought under control and subsequent inflammation reduced. Apart from anti-inflammatory drugs, swelling may be reduce by cortisone injections.
Patients who are pessimistic regarding the inability to use their wrist properly may benefit from tricyclic antidepressants. They usually need additional counseling in order to cope with depression initiated by the condition.
Physical therapy as well as occupational therapy are two more treatments necessary for the affected hand to regain its strength and for one to improve wrist range of motion. The most commonly prescribed exercises are grasping exercises, rotation exercises and rubber brand stretch.
Radial Nerve Palsy Surgical Therapy
In order to reach the radial nerve surgeons may apply the anterolateral approach, posterior approach or even the combination of the two. The decision basically depends on the affected part of the nerve. Surgical treatment is especially important for individuals in whom damage to the nerve is caused by bony projections striking the nerve.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...