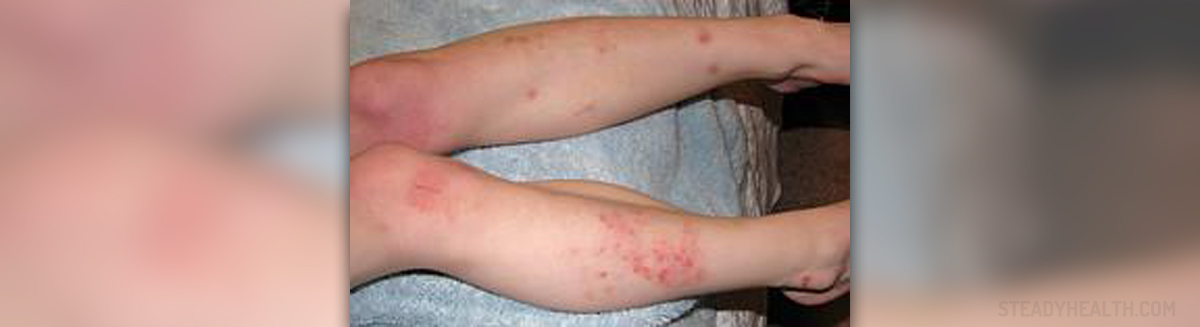
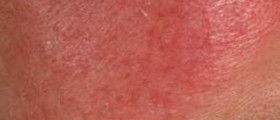
Eczema is a skin condition that causes dry, itchy and red patches of skin that itch. This skin condition comes in flare-ups and it is vital to know how to manage them so they can pass as quickly as possible and with the least discomfort.
Therapy for eczema
Dryness, which is one of the main symptoms of eczema, can be efficiently managed with regular use of moisturizers. The skin needs to be well-lubricated and nurtured so it is recommended to apply moisturizers several times a day. It is believed that eczema flare-ups can even be prevented by moisturizing regularly.
Eczema is an inflammatory condition and when the flare-ups occur they are traditionally treated with medications that suppress inflammation, such as topical corticosteroids. These medications come in different strengths and the best way to use them is to apply the least potent product that is effective. Using very strong corticosteroids is not recommended unless it is absolutely necessary.
Lichenification is another sign of eczema and it involves dry, hardened skin that resembles bark or leather. Initially, lichenification is treated with corticosteroids and in case of very itchy lichenified skin it is sometimes necessary to cover the area with bandages, which allows the topical steroids to work and also prevent scratching, breaking the so called itch-scratch circle. There are special bandages for this purpose and sometimes they contain ingredients such as zinc, coal tar or ichthammol.
The skin affected by eczema breaks easily, which makes it susceptible to infections. Staph infections are the most common ones, but fungal infections are also commonly seen in people with eczema. Such infections must be treated with appropriate medications, which means antibiotics and anti-fungals.
Unresponsive eczema
Eczema comes in different forms and levels of severity. Sometimes it cannot be managed with moisturizers and topical steroids and there are various treatment options for that case.
Oral corticosteroids are sometimes prescribed when topical ones fail to manage the flare-ups. Immunosuppressants, like cyclosporin or methotrexate, can also be used.
Light treatment of phototherapy is also an option for severe or unresponsive eczema. Exposure to sun or UVB light therapy in dermatological centers was found to be helpful even in such severe cases.
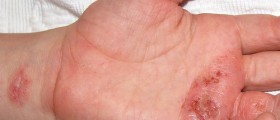
Chronic hand eczema is a type of eczema that is particularly hard to treat, even with oral medications. Alitrentinoin is one of the latest treatment options for this particular type of eczema but it is still fairly new and not yet widely used.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...