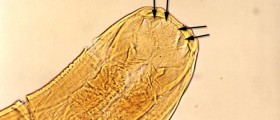
The tapeworm belongs to a group of flatworm parasites that infect both man and animals. The infection they carry is taeniasis and cestodiasis, are called zoonotic as they transmit from pigs, cows, fish and dogs to man. These infections mostly occur in underdeveloped countries where people consume raw, unwashed and undercooked meat containing the tapeworm cyst or eggs. As the human intestines present a good environment for the tapeworm to grow, it spreads through the oral/anal route and can grow up to 15 to 20 feet in length. When the tapeworm reaches maturity, its cysts or eggs are excreted in the feces which contaminate the surroundings. That soil or excrement further infects the intermediate hosts such as pigs, rodents, cows and other animal which pass the cysts or eggs in their meat on to humans where the tapeworm can develop. Some symptoms of a parasitic tapeworm infection are weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite, bloating in the stomach, stomach upset or pain, but it is also possible that no symptoms are present.
These infections can be avoided by washing your hands thoroughly and practicing good hygiene, by properly disposing human and animal feces, and checking and deworming domestic animals regularly. All meat should be well cooked to kill off the cysts at the temperature of 135 degrees Fahrenheit, or by freezing meat products for longer periods of time for at least 12 hours.
If a cyst ends up in the human body it can cause cysticercosis, a condition where a cyst is lodged somewhere in the brain causing seizures, swelling, dementia and other difficulties. It can be found in the muscles too, making lumps under the skin. If it is located in the eye, it causes blurred vision and detachment of the retina. In the heart, it can make lesions resulting in abnormal rhythm and heart failure. In the spinal cord it can form lesions resulting in loss of motor control, weakness and even paralysis. Anti-inflammatory drugs are also given to reduce swelling and vitamin B-12 shots to treat megaloblastic anemia.
A grown tapeworm is treated with drugs, aimed at killing off and later expelling the tapeworm from the body. Surgery is applied to remove the cysts or to the whole tapeworm in more severe cases. After 48 hours of treatment with antihelmintic drugs, the tapeworm and eggs start appearing in the feces. The follow-up stool samples are analyzed for the following three months to make sure the treatment was successful.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...