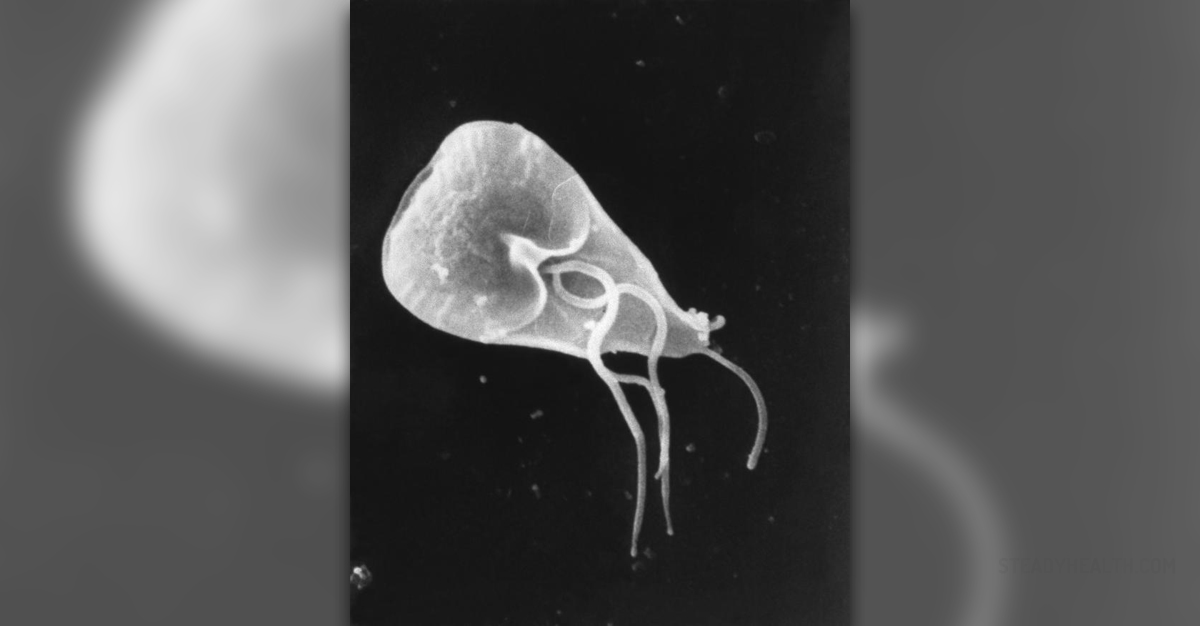
Giardia is a protozoan parasite that can inhabit the human gastrointestinal tract and cause an infection called giardiasis or beaver fever.
About giardiasis
Giardiasis occurs after a person swallows a giardia cyst, contracted through contact of infected feces of animals like beavers, dogs, cats, mice, rats and cattle. Giardia cysts can survive in cold water for several months, the infection can occur by drinking contaminated water. After the cysts are ingested, they rupture and the parasite colonizes the upper small bowel.
However, not everyone who has giardia in the intestine will exhibit symptoms. This infection is often asymptomatic, and symptoms usually develop in people who have a compromised immune system, who suffer from another disease or malnutrition, and people who have the blood group A are more prone to symptomatic infection than other blood types.
If the symptoms do occur, they include diarrhea, cramps, flatulence, fever, greasy stool, nausea, bad breath, heartburn, bloating, loss of appetite, malaise and fatigue.
Treatment for giardiasis
If the doctors suspect a patient may suffer from giardiasis, it is necessary to confirm it through diagnostic tests. The main test used for this purpose is ELISA, which is a lab test that looks for antibodies or antigens in the sample. The stool is also checked for eggs and mature giardia.
If the giardiasis is confirmed, the first step is to see if the patient is dehydrated and, if so, to administer intravenous crystalloid fluids, along with oral intake of fluids.
After this, antimicrobial medication is prescribed or administered to treat the infection and to basically kill the parasite. Doctors will also need to see and inspect the patient’s close contacts because they might be infected as well.
The first line of treatment includes metronidazole, tinidazole and nitazoxanide, and alternative medication may include paramomycin, albendazole, furazolidone and several other drugs.
Metronidazole, the most commonly used antimicrobial drug for giardia, has a cure rate of 80 to 90 percent and the treatment usually lasts from five to seven days, after which time the tests are repeated to check if the infection is indeed gone.
Tinidazole, which as recently been approved for use in the United States, has 90 percent efficiency rate and fewer side effects that metronidazole.
There are several drugs that are even more effective, like quinacrine, which has a 95 percent cure rate, but they have not been approved in the United States.
As for the side effects, tinidazole may cause an upset stomach, while quinacrine lists nausea, vomiting and cramps as possible side effects.







_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...