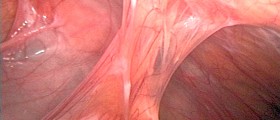
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix a worm-like pendant attached to the cecum which is the proximal part of large intestines. Having no function at all this pendant might get inflamed and then lead to an operation. The worse thing that can happen is the perforation of the appendix which is a highly serious condition.
Appendicitis is quite a common condition affecting both young and old generations. Still, the children develop the state in most cases. The highest incidence is among young men between 10 and 14 and girls between 15 and 19 years of age. The pain in the abdomen is the main symptom. It is strong and severe sometimes located in the lower right area of the abdomen and most of the time it irradiates and spreads on the whole abdomen.
- We searched MEDLINE and EMBASE databases for population-based studies reporting the incidence of appendicitis or appendectomy. Time trends were explored using Poisson regression and reported as annual percent change (APC) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). APC were stratified by time periods and pooled using random effects models. Incidence since 2000 was pooled for regions in the Western world.
- The search retrieved 10,247 citations with 120 studies reporting on the incidence of appendicitis or appendectomy. During the 21st century the pooled incidence of appendicitis or appendectomy (in per 100,000 person-years) was 100 (95% CI: 91, 110) in Northern America, and the estimated number of cases in 2015 was 378,614.
- The pooled incidence ranged from 105 in Eastern Europe to 151 in Western Europe. In Western countries, the incidence of appendectomy steadily decreased since 1990 (APC after 1989=?1.54; 95% CI: ?2.22, ?0.86), whereas the incidence of appendicitis stabilized (APC=?0.36; 95% CI: ?0.97, 0.26) for both perforated (APC=0.95; 95% CI: ?0.25, 2.17) and nonperforated appendicitis (APC=0.44; 95% CI: ?0.84, 1.73).
- In the 21st century, the incidence of appendicitis or appendectomy is high in newly industrialized countries in Asia (South Korea pooled: 206), the Middle East (Turkey pooled: 160), and Southern America (Chile: 202).
Ruptured Appendix Diagnosis
The complete blood count may point to an increased number of white blood cells. The patient feels nausea and may vomit or develop diarrhea. In all the patients every other condition must be excluded before the definite diagnosis of appendicitis is set since there are a lot of states that mimic the inflammation of the appendix. This is to be done urgently as the appendix may burst and cause severe complications.
In women pelvic inflammatory disease, ruptured ovarian follicles or cysts, tubal pregnancies or endometriosis may mimic acute appendicitis. Sometimes the diagnosis is not certain until the operation is performed. The surgery is recommended without postponement if the symptoms are clear. If not it may be delayed until the definite set of diagnoses.
The Importance of Treatment
The specific sign about the rupture is that pain vanishes instantly. A sign of rigid abdominal muscles may also point to the rupture. The body temperature is high. The heart beats faster. The condition is serious as the content of the appendix is spilled into the peritoneum (abdominal sack containing intestines and abdominal organs).
This leads to peritonitis and if not treated on time may cause sepsis. The surgeon must perform the operation, resect the appendix and clean the inner surface of the peritoneum properly. High dosages of antibiotics are prescribed and administered and the healing process takes much longer than after the regular operation of appendicitis without rupture.
Patients are held in the hospital for a week or two and are advised to stay away from strenuous activities for at least a month.
So it is important for a doctor to set the correct diagnosis of appendicitis on time. Correct diagnosis leads to the safe removal of the inflamed appendix (appendectomy) and reduces the chance of appendix perforation.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...