Rebound tenderness is actually a pain which occurs upon removal of pressure from the abdomen. It can be discovered during a physical examination/ palpation of the abdomen. This sign is generally associated with irritation of the parietal layer of the peritoneum.
Rebound tenderness is a sign of many medical conditions of the internal organs, to be more precise abdominal organs and some reproductive organs. It can also affect people suffering from sickle cell crisis and those with injury of the abdomen.
Causes of Rebound Tenderness
Peritonitis is the most common cause of rebound tenderness. The peritoneum is the serous membrane which lines the inner wall of the abdomen and pelvis. If it gets inflamed the condition is medically known as peritonitis. The inflammation of this serous membrane may develop as a consequence of microbial infection, trauma to the abdomen or abdominal bleeding. Peritonitis may be also a feature of several illnesses such as systemic lupus erythematosus, familiar Mediterranean fever and porphyria.
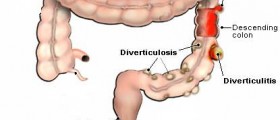
Appendicitis is another possible cause of rebound tenderness. Once the appendix gets inflamed it may irritate peritoneum or in case it ruptures the entire peritoneum may be affected with inflammatory reaction which subsequently results in rebound tenderness. Rebound tenderness is also a feature of diverticulitis. This is inflammation of diverticula small pouches that form inside the large intestine. Pancreatitis and gastritis also lead to rebound tenderness. The very inflammation of the pancreas and the stomach is very painful and rebound tenderness even tends to intensify in a case of any complications associated with either pancreatitis of gastritis.
Sickle cell crisis features with two phenomena: hemolytic crisis and vaso-oclussice crisis. The condition has many symptoms and signs, and abdominal pain in a form of rebound tenderness is only one of them.
To sum up, any condition of the organs in the abdomen or pelvis which is accompanied by inflammation of the particular organ or in case it leads to inflammation of the peritoneum may eventually cause rebound tenderness.
Diagnosing Rebound Tenderness
Rebound tenderness is easily confirmed with examination (palpation) of the abdomen. A doctor applies a gentle pressure on the abdomen and then removes the hands suddenly. If one feels an increase in the abdominal pain after the examiner's hands are lifted, rebound tenderness is confirmed.
What follows is further examination which will reveal the underlying condition so that the proper treatment can be prescribed.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...