
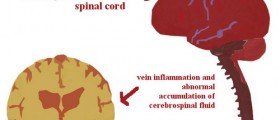
Waterborne diseases are diseases that are transmitted through contaminated water. They can be contracted by drinking water that contains pathogenic microorganisms- bacteria, protozoa, parasites, fungi, viruses.
If contaminated water is used for cooking, it can be the source of the diseases as well, except that in that case the disease is considered to be food-borne.
What are waterborne diseases?
Diarrheal disease is widely present, especially in countries with low sanitary standards, and it is responsible for 1.9 million deaths each year. In the majority of cases, this disease was transmitted through contaminated water.
Protozoal infections through contaminated water include amoebiasis, cyclosporiasis, giardiasis and cryptosporidiosis, among others. Common parasitic infections include ascariasis, enterobiasis, schistosomiasis, hymenolepiasis, taeniasis and others, while bacterial waterborne diseases, which are the most common, include botulism, campylobacteriosis, cholera, E. coli, dysentery, legionellosis, leptospirosis, salmonellosis and typhoid fever. Viral waterborne diseases include gastroenteritis, hepatitis A, adenovirus infections, SARS and poliomyelitis.
Some of the waterborne diseases are very serious and potentially fatal, while others go away on their own within several days and leave no considerable consequences. Regardless of that, it is clear that all possible efforts must be made to prevent these diseases.
Prevention of waterborne diseases
The main step in prevention of waterborne diseases is the practice of good hygiene and ensuring that all the family members follow the same hygienic guidelines. It is particularly important to wash hands regularly, with soap and warm water, especially after using the bathroom or before meals. If the tap water is suspected to be contaminated, special hand sanitizers in form of gel or liquid should be used.
The water used for drinking must be properly filtered. This applies also to the areas where tap water is generally considered to be safe. In areas with highly polluted tap water, only bottled or boiled water should be used for drinking and for cooking.
Containers used for storing clean drinking water should be either washed or replaced every day. Fresh water must not be added to containers with stale or unclean water.
Only food that has been thoroughly cooked should be consumed. Fresh fruit and vegetables should be peeled and washed in clean water before eating.
It is also recommended to check if the pipes and taps that supply the water to the household are in proper shape. Unclean water wells must be emptied and cleaned.
Some waterborne diseases can be contracted by immersion, for example during swimming or diving. This means that it is very important to make sure the water in swimming pools, hot tubs and whirlpools is clean and without any pathogenic microorganisms. When swimming in rivers, creaks, ponds and lakes, it is recommended to check if they were controlled for microorganisms by the local health authority.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...