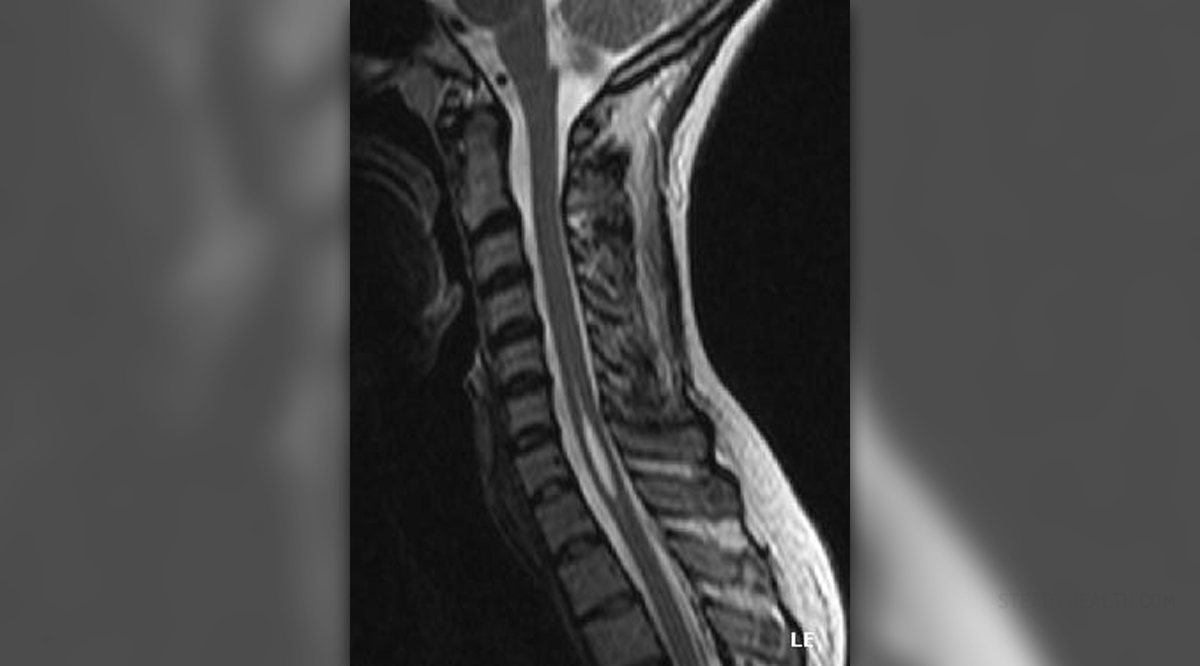
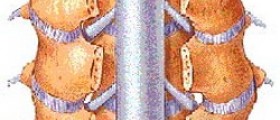
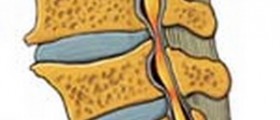
Syringomyelia is a neurological condition caused by damage to the spinal cord. Such damage develops as a consequence of the formation of a fluid-filled cyst known as syrinx. In the majority of patients the condition affects the cervical spine. While being small, a syrinx does not cause any problem at all. Its growth, however, is closely connected with many neurological signs.
Types of Syringomyelia
Syringomyelia may be classified according to the cause of syrinx formation.
Firstly, there are congenital brain defects that obstruct the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and initiate the formation of a syrinx. One of congenital brain defects frequently associated with syringomyelia is Arnold-Chiari malformation.
Secondly, syringomyelia may occur after some injury to the spinal cord. Trauma, infections like meningitis or HIV as well as compression of the spinal cord of different origin may all contribute to the onset of syringomyelia.
Finally, there is idiopathic syringomyelia, a condition with no identifiable underlying cause.
Syringomyelia Clinical Characteristics
Symptoms and signs of syringomyelia are not unique and they vary from one patient to another. They occur suddenly, but may progress slowly.
For instance, some patients experience pain and weakness in the back, shoulders and upper or lower extremities. Headaches, reduced or loss of skin sensation, muscle atrophy, incontinence and sexual dysfunction may occur as well.
Treatment for Syringomyelia
Initially, while the syrinx is small, patients may be only monitored and doctors opt for 'watch-and-wait' approach.
This medical condition cannot be cured with medications. Some of its symptoms, however, may be brought under control with certain drugs. This particularly refers to pain and muscle spasms. Pain is brought under control with a variety of pain killers while muscle spasms vanish with muscle relaxants.
Some patients may benefit from shunting, a procedure that involves insertion of a thin tube into the cyst. The tube helps the cyst to drain and the pressure to the spinal cord significantly decreases. Surgery is the only efficient treatment for syringomyelia and is recommended once the symptoms become unbearable or damage to the spinal cord may soon become irreversible. Surgeons remove the cyst. Sometimes, if the cyst is caused by a brain tumor, this growth is surgically removed as well. Left untreated syringomyelia may eventually cause paraplegia or quadriplegia.
Prevention of Syringomyelia
There is no efficient way to predict who will develop syringomyelia. Still, since it is known that certain injuries and infections may contribute to the condition, by avoiding these one may prevent syringomyelia from developing.
What is more important is prevention of complications syringomyelia itself brings. So, only timely performed surgery may prevent irreversible damage to the spinal cord and life-long neurological sequelae.



-And-Multiple-Sclerosis-Differences-And-Similarities_f_280x120.jpg)


-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...