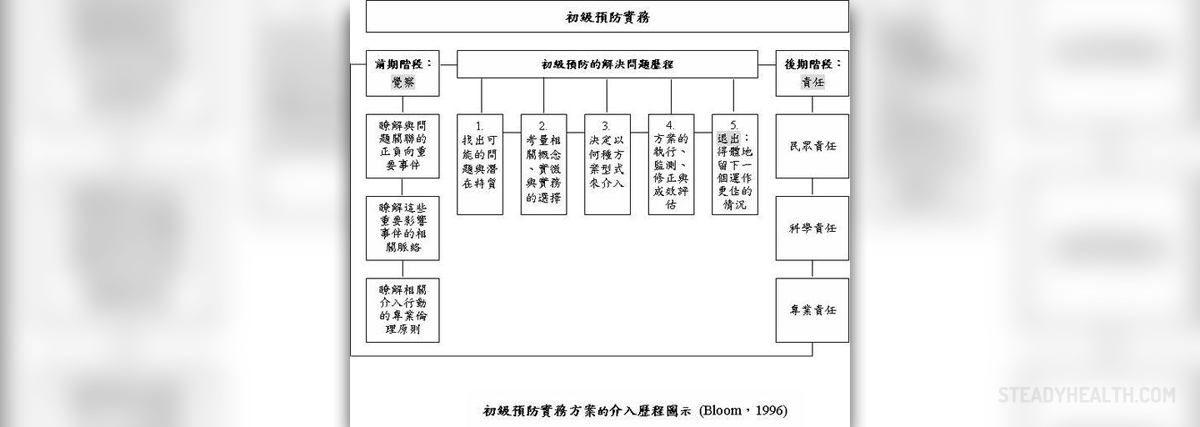
In some cases, the HIV virus can be transferred from a mother to a child during pregnancy, birth or breastfeeding. However, there are certain risks which can be prevented by putting the right measures into action. In some countries, transmission of HIV from a mother to a child is a very common issue and people are doing their best to stop this or reduce the frequency of this occurring.
The Program
In most hospitals, clinics or Midwife Obstetric Units, pregnant women can undergo HIV tests and get proper counseling and information on the subject, learning more about this virus and its characteristics. If a mother learns that she is HIV positive after the test results come, she can enter the Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission Program or PMTCT for free. Most of the clients in this program receive Zidovudine from 28 weeks of pregnacy, Nevirapine during labor and Zidovudine 3 hourly in labor. This is the case with mothers who have CD 4 count larger than 250. If this number is smaller, the mother will receive HAART therapy.
Once born, the baby will be supplied with Zidovudine and Nevirapine syrup for one week or month, if the mother received the antiretroviral treatment during her pregnancy.
You have to be aware that, even though these medication will reduce chances of mothers transferring the HIV virus to their babies, chances of this happening will still be from 60 to 85%. Also, if the child gets infected by the virus during pregnancy or through breastfeeding, antiretroviral medications will not help. Finally, these medications are not capable of curing this condition. Rather, they can save the child from contracting HIV in some cases.
How To Protect Your Child
Through counseling, HIV mothers will learn that they need to either breastfeed the child exclusively or to feed it with formula. In case of latter choice, the PMTCT will provide the mother with the necessary formula discount for six months. Yet, whichever choice a mother may opt for means that she should never feed her child with tea, water, juices or solid food, since this will increase chances of the baby contracting HIV.
Once a mother suffering from HIV gives birth to a baby and becomes a part of this therapy, she should visit a follow up clinic every one or two weeks. During these visits, the baby's weight will be monitored and recorded. Also, immunization procedure will be carried out, and pneumonia prevention therapy administered. Finally, feeding methods will be analyzed and checked. After 6 weeks of this routine, the baby will be tested for HIV. If the child is not infected by HIV, he/she will no longer undergo immunization therapy. However, if the results are positive, he/she will have to start on the HAART therapy.
Finally, mothers are advised to stick with the therapy and undergo regular checkups. Also, they need to stay protected and use condoms and other adequate contraception.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...