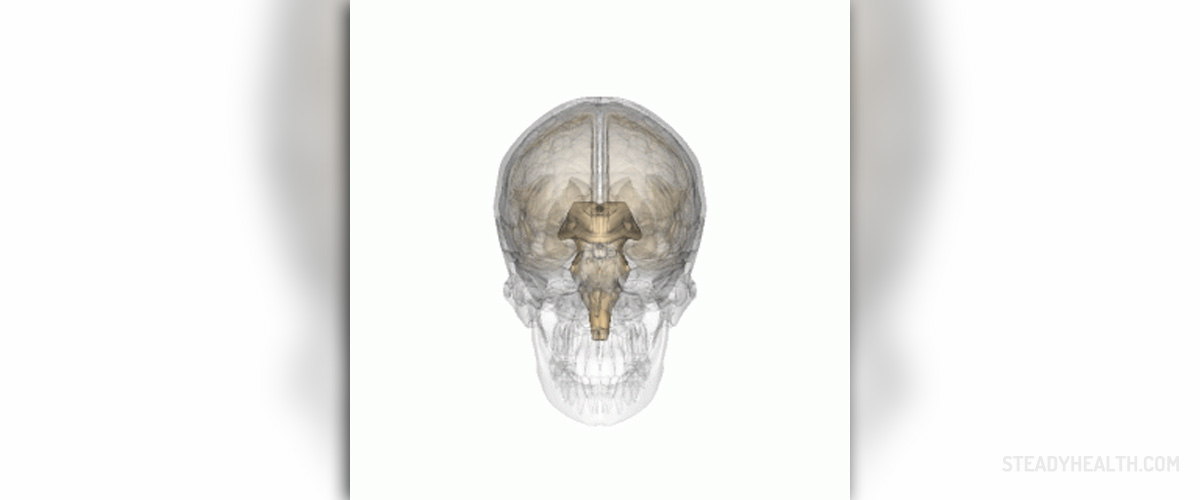
The pineal gland, also called pineal body, is a small endocrine organ, positioned at the center of the brain, in between the two hemispheres. Its major role is to secrete melatonin, a hormone responsible for sexual development, metabolism and sleep-wake cycle. The pineal gland is a photosensitive organ and its function is inhibited by light. On the other hand, production of melatonin hormone is stimulated by darkness.
A cyst in the pineal gland is a fluid filled mass with sac-like appearance. They are benign (non-cancerous) structures that often do not cause any problems and many people with a pineal gland cyst are not aware of their presence. However, in some patients a pineal gland cyst may grow in size, causing them to experience symptoms such as headache, vertigo and others, when the cyst enlarges enough. A pineal gland cyst is one of the three types of pineal region lesions, along with germ cell tumor, pineal parechymal tumor and metastases.
Pineal Gland Cyst Symptoms
As already mentioned, pineal gland cysts are generally asymptomatic. However, when they grow larger than 0.5 cm in diameter the cysts can cause different symptoms. The person with a cyst in the pineal gland will most commonly experience headaches, vertigo, nausea and vomiting. Visual disturbances and increased sensitivity to light are also common. Sometimes, the pineal gland cyst may grow large enough to cause hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus is a condition marked by a build up of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain. It can result out of the pineal gland cyst compressing the cerebral aqueduct, a fluid filled passage within the brain. Obstructed flow of cerebrospinal fluid causes pressure to build up in the brain. This can result in headaches, nausea, vomiting, lethargy and sometimes ataxia and coma. Seizures may also sometimes occur as a result of the pineal gland cyst.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pineal Gland CystSince pineal gland cysts most often do not cause symptoms and health problems, they are usually discovered incidentally during CT or MRI scan of the brain for another reason. More frequently, pineal gland cysts are detected in people autopsied after death.
Large pineal gland cysts that cause symptoms require prompt neurological evaluation and brain scan. On an MRI scan these cysts are easily distinguished by their characteristic appearance form other tumors of the pineal region.
Pineal gland cysts usually do not require any treatment since they are benign and asymptomatic. On the other hand, if the pineal gland cyst grows very large and causes severe symptoms, the treatment may involve surgical removal of the cyst. Also, if the cyst does not cause serious problems, the treatment may include medications to relieve the symptoms.
- www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/dark-matter-dna-active-brain-during-day-night-cycle
- www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/cysts
- Photo courtesy of Life Science Database by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pineal_gland.gif














Your thoughts on this
Loading...