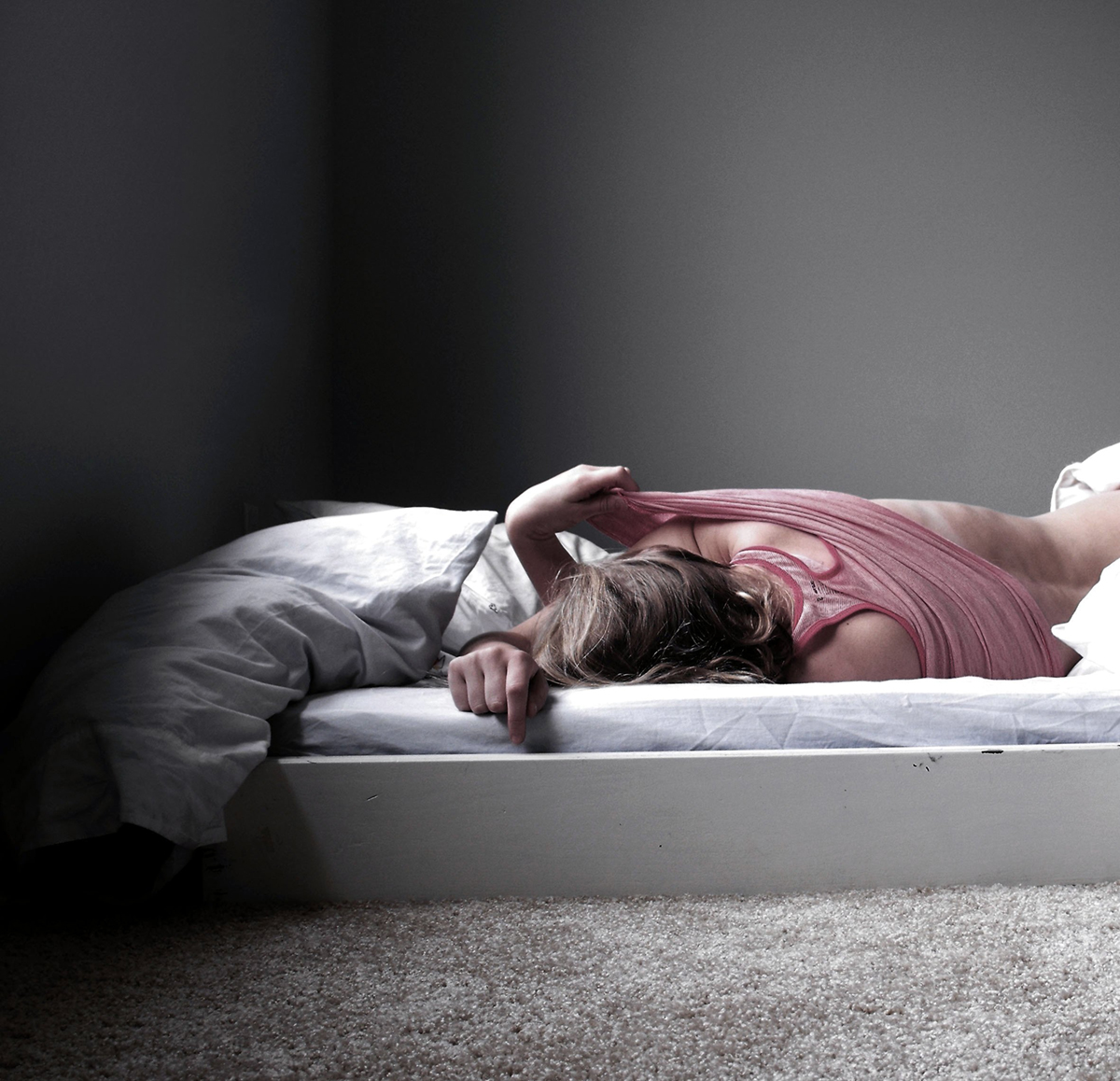

Dysmenorrhea, menstrual cramping or painful menstruation are terms used to describe the pain and discomfort that occur to some women during menstruation. The pain can be either sharp or dull, and it is usually located in the pelvis and lower abdomen and sometimes in the lower back.
Dysmenorrhea affects about 50 percent of all the women who have menstruations, and about 10 percent of them are incapacitated sometimes for as much as three days. Painful menstruation is the number one reason for missing school days or work among the menstruating women.
There are two types of dysmenorrhea-primary and secondary dysmenorrhea.
Primary dysmenorrhea
Primary dysmenorrhea means menstrual cramping in healthy women, who have no problems or conditions affecting their reproductive organs.
The factors which may increase the risk of primary dismenorrhea include having never given birth, obesity, smoking and family history of menstrual cramps.
In women who suffer from primary dysmenorrhea the uterine muscles are overly active and they contract a lot and frequently. Prostaglandins that are released during menstruation are believed to be the biggest contributors to painful menstruation in otherwise healthy women.
The cramping usually starts a few hours before the bleeding and may continue throughout the day or for several days. Other symptoms that may accompany the pain are fatigue, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
The treatment for primary dysmenorrhea, if needed, consists of over the counter pain relievers. Doctors usually recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) like ibuprofen and naproxen, and for patients who are not allowed to take NSAIDs the alternative may be a cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor.
Some women take oral contraceptives, which are known to reduce the pain associated with the menstruation by reducing the flow of blood and suppressing the ovulation.
Secondary dysmenorrhea
Secondary dysmenorrhea means that there is a medical condition present that is causing the pain and discomfort during menstruation. The conditions associated with secondary dismenorrhea are endometriosis, pelvic inflammation, ovarian cysts, pelvic congestions, fibroid tumors and adenomyosis.
Other causes may include the use of intrauterine device form of contraception and, for some women, the use of tampons.
Another difference between the primary and the secondary dysmenorrhea is that in secondary dysmenorrhea the pain is not necessarily associated with the time around the menses and can occur at other times during the cycle.
The treatment for secondary dysmenorrhea, apart from the medication administered to relieve the pain, consists in identifying and treating its underlying cause. The treatment will depend on the specific cause.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...