Introduction
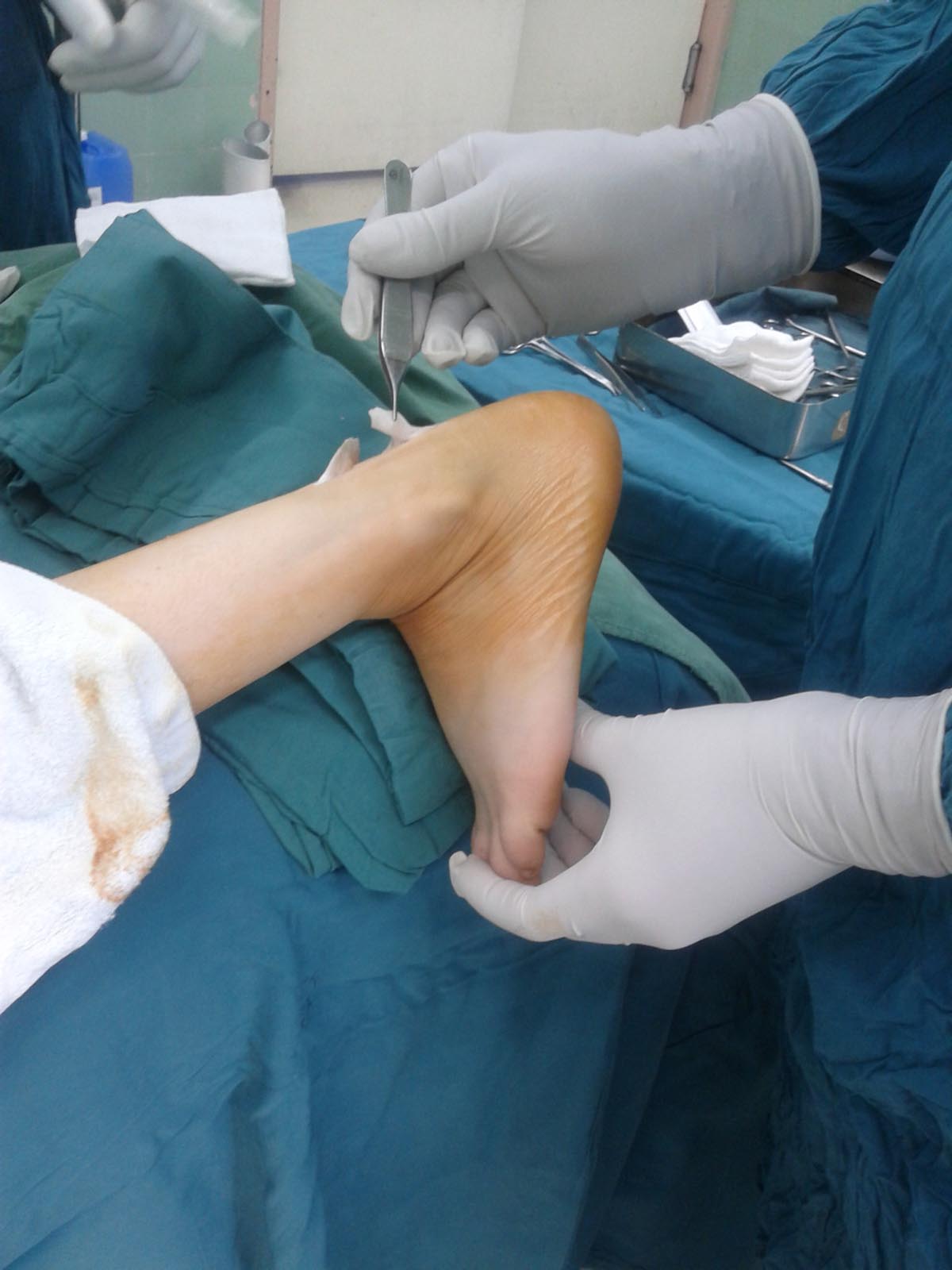
Most people experience pain behind the heel at some point oftheir lives which makes the condition extremely common. The area is importantbecause that is where the motion of the leg actually gets transferred to becomethe motion of the foot. The pain behind the heel can be a very disablingcondition. The two most important areas here are the heel bone and the Achillestendon.
The tendon got its name from the Greek warrior from the Bronze Agewhose heels were the only unprotected parts of his body. The Trojan princepierced his heel with an arrow and tendon is named after the event because itsdysfunction can affect one’s ability to walk and the overall ability tofunction properly.
Causes
The pain located behind the heel is usually triggered by theinflamed Achilles tendon or inflammatory conditions causes by bone growth inthe heel bone. Tendonitis is common and it gets worse by extended activity. Itcan be developed by chronic tendon stretching, violent injuries, blunt pressureon the heel back, and unbalanced motions.
Microscopic tears get developed veryeasily and they progress into larger tears. The tendon may rupture if thetendonitis is caused by an injury. The pain can be sharp, aching, throbbing ordull and it gets better with rest but it can easily come back with simpleactivities and motions. The bone attached to the tendon can also make a generalcontribution to the aforementioned condition as the spurs develop on the backof the bone.
When the inflammation kicks in, the spurs create an irritatingsurface which can make the inflammatory condition even worse when the tendonmoves over it. The spurs can even sometimes get fractured. These spurs are notthe same heel spurs which occur at the heel bottoms. Some people have anenlargement of the rounded top surface of the heel bone, medically referred toas Haglund’s deformity.
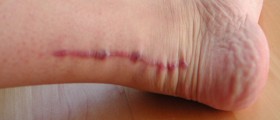
This condition also contributes to the irritation ofthe tendon. When left untreated the condition can lead to ruptured and torntendons which can easily be recognized by an inability to walk. Treatmentrequires stretching, icing, ankle bracing and physical therapy accompanied bymedication for the treatment of inflammations. Sometimes a person needs to beimmobilized in a walking cast, while some severe cases involve walking withcrutches. Untreated tendonitis may lead to rupture or numerous degenerativeconditions which may require surgical interventions.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...