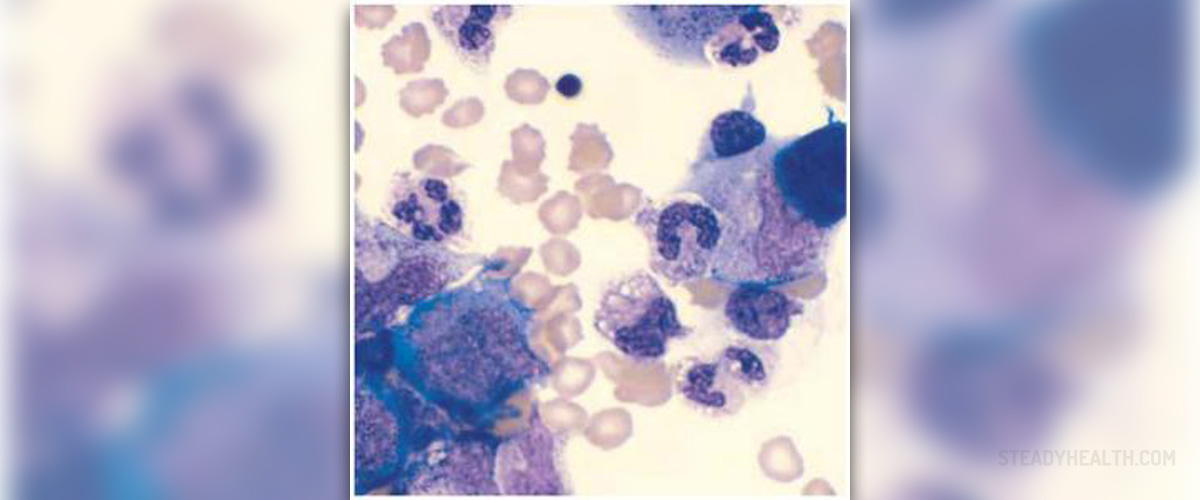
Osteosarcoma is the most frequent type of bone cancer. The tumor originates from osteoblasts, the cells responsible for growth of the bone tissue. It develops in bones and eventually spreads via blood stream to lungs or even other bones in the body.
Osteosarcoma predominantly affects teens and is more frequent among boys. The tumor develops due to random and unpredictable errors in the DNA and this is why it generally affects people during the most intensive growing part of their lives. Unfortunately, there is no definitive cure for osteosarcoma but if the disease is diagnosed on time patients may have good prognosis.
Clinical Features of Osteosarcoma
The most common characteristics of osteosarcoma are pain and swelling in the affected bone. In majority of cases the tumor affects long bones such as the femur or the humerus. The pain becomes more intensive during exercise and at night. The growth of the tumor eventually leads to visible lump and swelling. The pain becomes more intensive in time and eventually drives a patient to see a doctor. If the tumor affects the bones in the leg the child may start to limp. In many cases the growth of the tumor may cause fracture of the affected bone.
Diagnosing Osteosarcoma
After thorough physical examination patients undergo additional tests and exams among which the most significant ones are imaging methods such as X-ray, CT scan and MRI of the affected part of the body. Once the tumor is identified by some of the previously mentioned it is biopted and definitive confirmation is achieved with pathohistological examination of the biopted tissue.
Treatment for Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is treated with surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. The cornerstone of treatment is surgical resection of the tumor. It is essential to remove the entire tumor and surgeons also remove even the healthy tissue around the tumor to be sure that even the microscopic components of the tumor have been completely removed. Since there is a chance that some of the tumor cells have remain in the operated area patients are additionally treated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy can be also administered prior the surgery. The goal of chemotherapy is to deal with cells of the tumor that might have spread to the rest of the body while radiation therapy is performed to sterilize the operated area. Chemotherapy is also treatment modality in case of metastatic spread of the disease. The prognosis develops on several factors. Unfortunately, the disease is not curable and treatment only provides with certain extent of remission.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...