Methotrexate is a medication that is commonly used in treatment of a cancer. Methotrexate is used in managing lymphoma and certain types of leukemia. Breast cancer, uterine cancer, lung cancer, brain cancer and ovarian cancer are also treated with this medication. Furthermore, it can be prescribed to patients with rheumatoid psoriasis and psoriasis. It has been proven effective even in inducing miscarriage in females with ectopic pregnancy. Methotrexate must be used in prescribed dosage to avoid serious and life-threatening side effects of the drug.
Methotrexate Effects
Methotrexate is classified as the disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs or DMARDs. This drug inhibits progression of rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic disorders, thus it prevents further damage to the joints. Methotrexate interferes with the growth of cells that reproduce rapidly like cancer cells, skin cells and bone marrow cells. The drug also blocks enzyme dihydrofolate reductase that is involved in the immune system, which inhibits the metabolism of form of folic acid. This folic acid plays a vital role in growing cells in the blood, skin, gastrointestinal tract and the immune system. That is why methotrexate is given for treatment of cancer and psoriasis. It is helpful in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis since it alters immunity although exact mechanism of action in this disease is not fully understood. The drug is given to patients that have not responded to other drugs or treatments.
Methotrexate Dosage
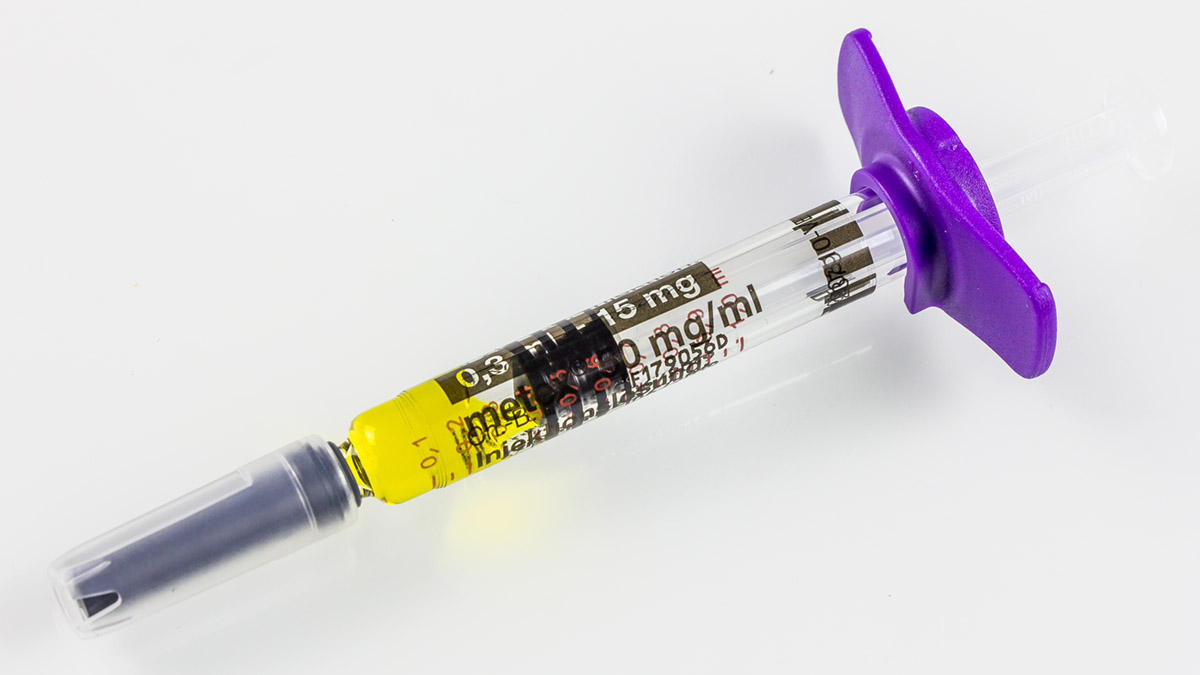
Patients must take the medication for their condition in dosage as ordered by a doctor. The dosage for cancer is a little higher than dosage for psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis. If a dose is missed, it must be skipped and taken in time for the next dose. Two doses at once should never be taken. Methotrexate can be given in form of injection or tablet. The tablets are available in doses of 2.5, 7.5, 10 and 15 mg. The dose can in some cases be as high as 20 to 25 mg per week. The dose of methotrexate higher than 17.5 mg/week is commonly given in a form of injection that may be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
Methotrexate Side EffectsCommon side effects of methotrexate include cough, diarrhea, nausea, headache, drowsiness, appetite loss, skin rash, lung problems, shortness of breath, sun sensitivity, dizziness, itching and hair loss. Serious side effects include blurred vision or sudden vision loss, weakness, seizures, confusion, and loss of consciousness. In high doses, methotrexate can cause mouth sores, upset stomach, low white blood cell count and severe toxicity of the liver, kidneys and bone marrow.
Precautions
Pregnant women and those who are planning to get pregnant should not use methotrexate. This is due to possible cell damage in fetus that may result in birth defects. Patients with kidney or liver problems must also avoid the drug.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...