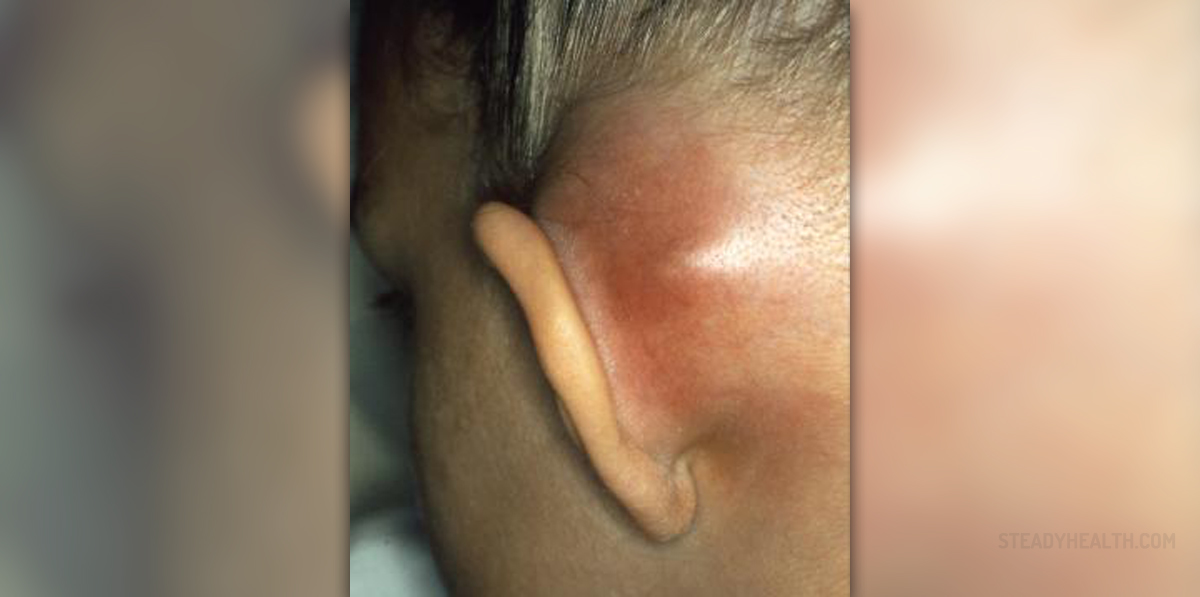
What exactly is mastoiditis and what symptoms indicate it?
In order to understand what mastoiditis is, it is necessaryto know that there is a part of the temporal bone in the skull (to be more precise, right behindthe outside ear) and this part is filled with open cavitiesthat contain air. Inflammation of the mastoid air cell is called mastoiditis,and in the greatest majority of the cases, it is caused by some bacterialinfection of the inner ear. Since this infection can easily spread to other structuresin the surroundings and thus cause much more serious problems and even permanentconsequences (particularly if it spreads to the brain), it is more thannecessary to treat it. This is exactly why mastoiditis used to be one of themost frequent causes of mortality in children before the antibiotics becamewidely available.
As for the symptoms through which this condition manifests,those that are inevitable are pain and tenderness in the affected region (behindthe ear), although swelling can be present as well. Pain might be present inthe ear too, which might also become red. Very common are headache and fever,although these symptoms are usually not present in cases of children. They tendto have symptoms that do not really indicate problems with the ear, and some ofthem are anorexia, diarrhea and irritability.
How can it be treated?
First of all, it is necessary to know that this condition,if present for too long and untreated, might result in the damage to thedelicate mastoid structures, which usually leads to the loss of hearing. Also,the bone in the skull might be seriously damaged if the condition in questiondoes not get appropriate treatment soon enough. Complications that are commonin cases of children include meningitis, labyrinthitis, and even facialparalysis, which in general implies the seriousness of the problem and necessity of thetreatment. This goes for any ear infection, because timely and adequatetreatment of ear infections is a very simple and easy way in which mastoiditiscan be prevented.
As for the treatment, antibiotics are inevitable, but some casesrequire the drainage of the fluid that is accumulated. More severe cases requiremastoidectomy, a surgical procedure that consists of removing the destroyedbone and cleansing the area in question. Very rarely, in cases in which theloss of hearing is evident, radical mastoidectomy is necessary.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...