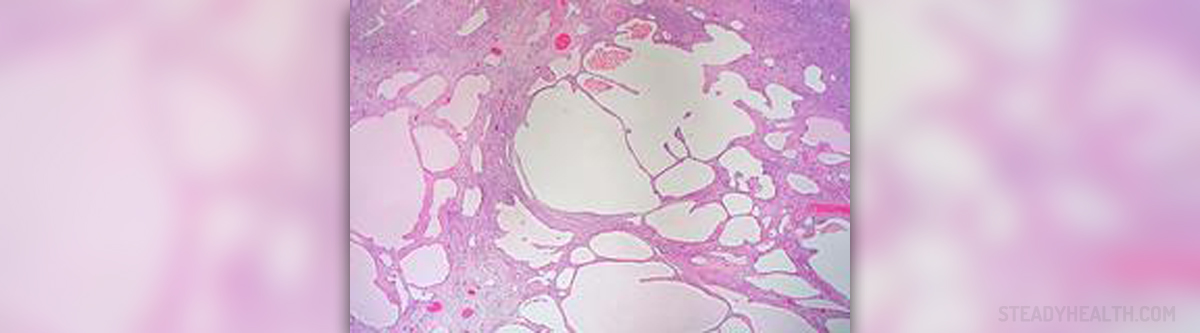
Liver or hepatic hemangioma is non-cancerous mass developed in the liver (as the very name suggests). Causes of this problem are still unidentified, but, so far, doctors know that the tumor is made of a tangle of poorly developed blood vessels in the liver. The same medical condition is also known as cavernous hemangioma and it has to be treated if it shows any signs or symptoms.
As we have mentioned, there is no specific cause of this medical condition discovered yet. Doctors suspect that people suffering from liver hemangioma have had it since their birth. These non-cancerous growths can vary in size and be about 5 cm (which is the most common size) or even larger. Also, a person might have just one or several hemangiomas.
In most cases, patients do not have any symptoms because the mass does not grow. So, it can be concluded that patients suffering from pains and other symptoms of this condition actually have a growing hepatic hemangioma.
Liver Hemangioma Symptoms
Patients suffering from hepatic hemangioma may experience fullness after eating even small portions of food. A mass present in the liver is found to be responsible for this and, therefore, many people eat something that a healthy person will not think of as nearly enough food. Nausea and vomiting are also very frequent in such patients as well as lack of appetite. Most people also experience upper right abdominal pain. Persistent symptoms of hepatic hemangioma must be reported to a doctor and treated accordingly.
Treatment Measures
Small hemangiomas which do not increase in size are not treated at all, especially if a patient does not have any health problems related to this issue. To avoid any complications a growing mass may cause, doctors advise regular checkups.
Hemangioma with symptoms must be treated. If the mass in the liver continues to grow, it could jeopardize the function of different organs in the abdomen and cause great discomfort. Doctors usually take into consideration the mass in the liver, its size, number of hemangiomas and their location as well as patient's general health. They may recommend surgical procedures in order to remove a part or complete hepatic mass or to cut off its blood supply. Liver transplant surgery is another option, saved for particularly severe cases of liver hemangioma when the tumor is extremely large and cannot be treated differently. Liver transplant surgery is actually very rarely performed because of this problem.
The last solution for hepatic hemangioma is radiation therapy which can damage the cells of hepatic hemangioma and stop their growth.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...