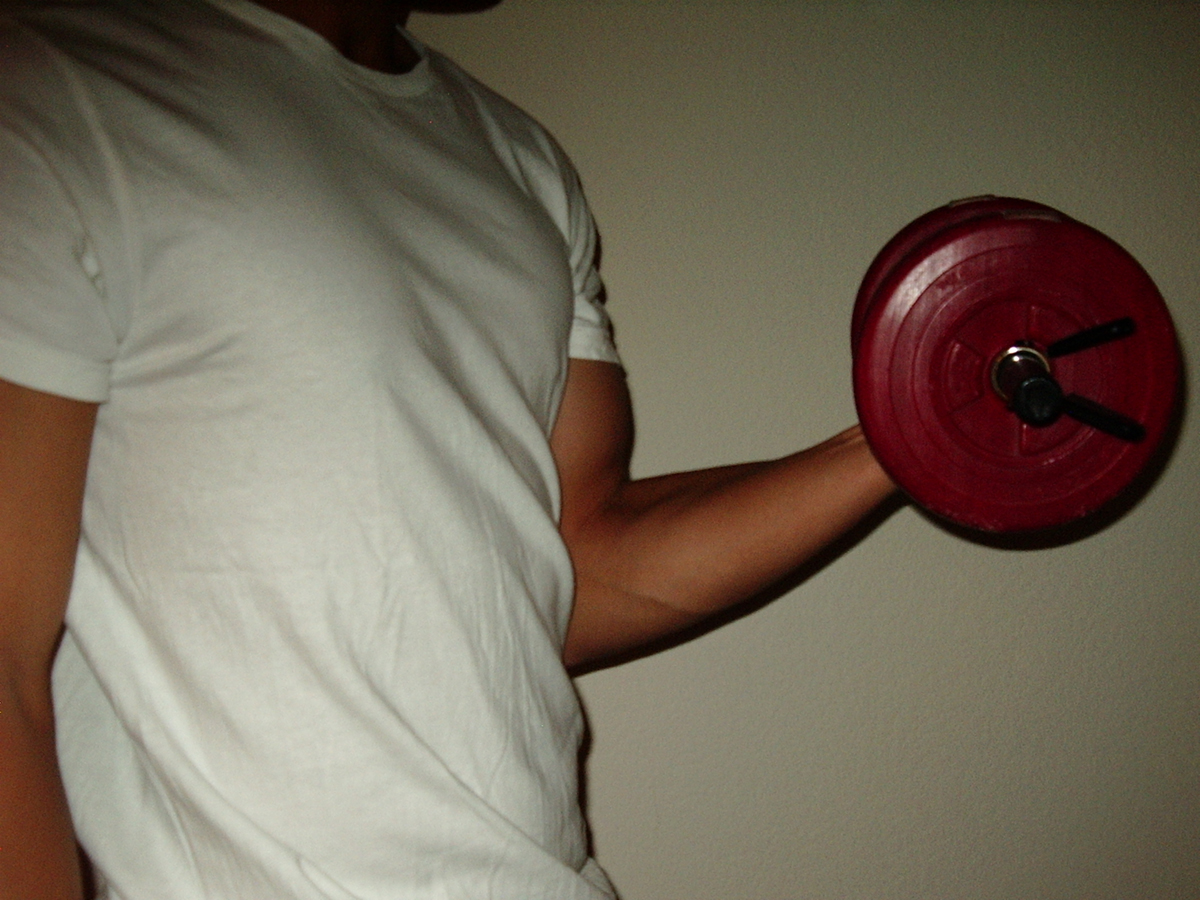

Role of muscles
Muscles can shorten their length by contraction. visibly, they become shorter and thicker. This is not bad for showing off, but there is much more to muscle contraction than just impressing someone. Muscles are meant to squeeze or move something when they contract. In example, the heart muscle squeezes the blood out, while skeletal muscles move the bone to which the insertion tendon is attached to (the one that does not move is the origin tendon). This causes motion.
Types of muscle contractions
There are two main types of muscle contraction. The first type is isotonic contraction. This is type of contraction in which the muscles contract and shorten while they produce force which causes movement of a body part. The second type is isometric contraction, when muscles produce force but do not change their length, as happens with muscles of your lower arm when you grip and hold something heavy.
How muscles work
Muscles are mostly water (over 70 percent) and protein (almost 22 percent). Proteins of muscle tissue are in form of thin strands of actin, and thick strands of myosin, which run the length of each muscle cell. Muscle contraction is basically sliding of actin and myosin protein strands over each other, which causes reduction of the length of the cell, and in turn, shortening of the entire muscle.
Muscle contractions are regulated by the central nervous system, and can be voluntary and involuntary (automatic, does not require - or offer - a conscious "order" to the muscle to contract). when a muscle should be contracted, the nerves which innervate its fibers receive the signal to act and transmit a weak electric impulse to the muscle cells. Once the impulse reaches the cells, it causes them to begin contraction. force of the contraction is determined by frequency of impulses that keep arriving from the nerve while the contraction lasts - the more impulses, the stronger the contraction.
How isotonic contraction works
In this type of contraction, tension remains constant while the muscle becomes shorter. these contractions are the most common in a majority of exercises and physical activities. All weight lifting exercises are based on isotonic contractions. to test how that works, flex and bend your biceps and measure its length before and after contraction. you will notice the significant decrease in length when it is contracted.
There are two types of isotonic contractions: concentric, where tension of the muscle increases to match the resistance and then remains on that level while the muscle shortens. The external force on the muscle is weaker than the force generated by the muscle in this case, and contraction causes muscle shortening. The other type is eccentric isotonic contraction, where the muscle lengthens as it contracts. this type of contraction typically serves to control or decelerate movement caused by the eccentric contraction. This type of contraction is stressful to the muscle and can cause injuries.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...