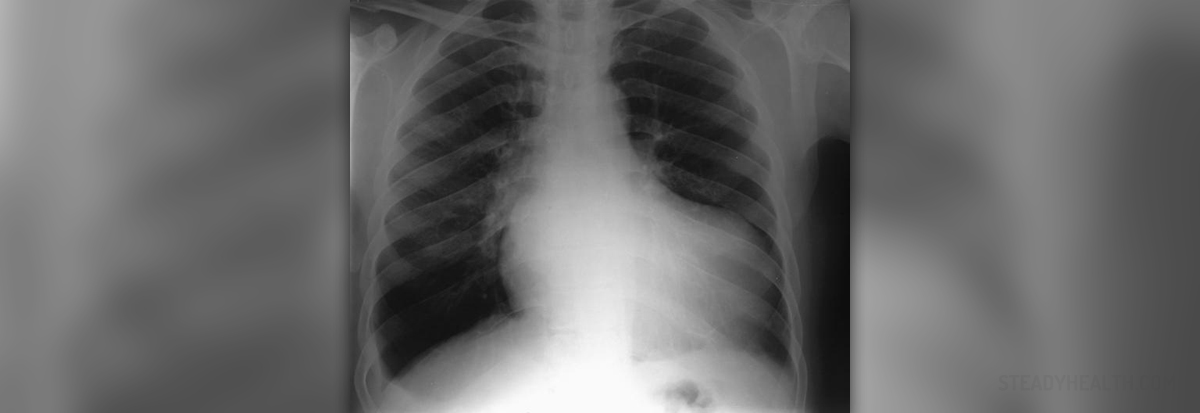
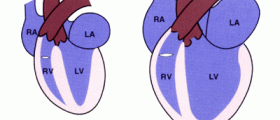
Enlarged heart, medically known as the cardiomegaly, is a condition which features with enlargement of certain parts of the heart (its ventricles or atria) or the entire heart becomes enlarged.
Causes of Enlarged Heart
In some cases the exact cause of heart enlargement cannot be identified and this condition is classified as idiopathic cardiomegaly.
On the other hand, this medical condition may result as a consequence of other illnesses. High blood pressure is, for example, one cause of heart enlargement. It may cause cardiomegaly if it lasts long enough and in case it is not properly treated. Heart valve disease is another cause of cardiomegaly. Improper functioning of the valves does not provide with proper flow of the blood and regurgitation of the blood may eventually cause heart enlargement. Cardiomyopathy is a heart condition which features with deterioration of the function of the myocardium and may eventually cause cardiomegaly. Furthermore, congenital heart defects, pulmonary hypertension and arrhythmia may also induce cardiomegaly.
Apart from heart disorders cardiomegaly may be a consequence of anemia, thyroid gland disorders, hemochromatosis and amyloidosis.
Symptoms of Enlarged Heart
Initially there are no symptoms or signs of enlarged heart and it may be only found accidentally during some routine examinations such as chest X ray. However, once the disease has progresses the patients commonly complain about breathing difficulties, shortness of breath, cough, dizziness, arrhythmia and swelling of certain body parts.
Treatment for Enlarged Heart
The best results are achieved in case cardiomegaly is detected on time. Still, this does not occur very often since as it has already been mentioned the disease is in the begging usually asymptomatic.
The goal of the treatment is to correct the underlying condition and to alleviate the symptoms caused by the heart enlargement.
Patients suffering from cardiomegaly are usually prescribed specific medications. They include diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme drugs, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta blockers and digoxin. Diuretics lower the level of sodium and water in the body hence reduce the blood pressure and swelling. Angiotensin-converting enzyme reduces the blood pressure and improves heart's pumping capability. Angiotensin receptor blockers are prescribed to patients who cannot take angiotensin-converting enzyme drugs. Beta blockers improve heart function and also reduce the blood pressure. And finally, digoxin is prescribed to improve the pumping function and prevent heart failure.
In patients whose symptoms cannot be brought under control with medications there are several surgical procedures. They include implantation of medical devices which regulate heartbeat (pacemakers, cardioverter - defibrillator), heart valve surgery and finally, if everything else fails, heart transplantation.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...