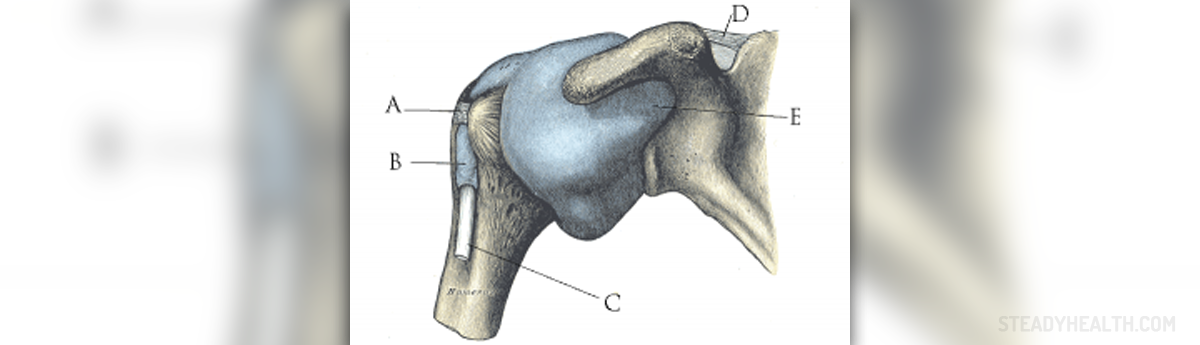
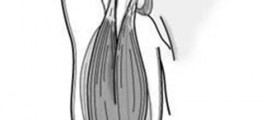
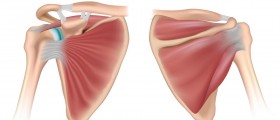
Shoulder dislocation represents separation of the humerus from the scapula. The shoulder joint possesses the greatest range of motions and this is what makes it rather susceptible to dislocation as well as any other injury. Dislocation can be total or partial. Partial shoulder dislocation is known as shoulder subluxation.
There are several types of shoulder dislocation and they include anterior, posterior and inferior shoulder dislocation. Anterior also known as forward shoulder dislocation occurs in more than 95% of cases. Majority of these dislocations are sub-coracoid. Other subtypes such as sub-glenoid, subclavicular, intratoracic and retroperitoneal may occur as well but very rarely. This type of shoulder dislocation may cause damage to the axillary artery. Posterior shoulder dislocation or backward shoulder dislocation is usually caused by strength imbalance of the rotator cuff muscles. It can be unnoticed. This is common for elderly people and those who have experienced trauma and are unconscious. The condition may remain undiagnosed up to a year. And finally, there is inferior shoulder dislocation. Inferior shoulder dislocation does not occur so often and accounts for approximately 1% of all shoulder dislocations. This particular type of dislocation features with the arm in permanent upward position. Inferior dislocation is a consequence of hyper abduction of the arm and carries significant risk of many injuries to nearby vascular and neurological structures and surrounding tendons and ligaments.
Signs and Symptoms of Shoulder Dislocation
The leading symptom of shoulder dislocation is the intensive pain in the shoulder which may sometimes radiate down the arm. The patient is unable to move the injured arm. There is also numbness of the affected arm. The injury is quite visible.
Treatment for Dislocated Shoulder
The treatment for dislocated shoulder must start promptly as soon as the diagnosis is set. Initially the injured shoulder is kept in the current position with the support of a splint or a sling. Cold compresses or ice may reduce the pain and swelling.
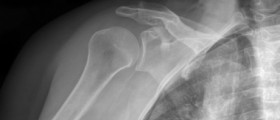
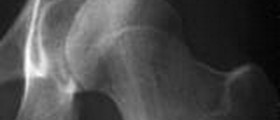
Once the patient is administered in the hospital the goal of the doctor performs physical examination and takes X-ray of the injured joint. Once the diagnosis is confirmed what follows is returning of the shoulder in its normal position. There are several methods of shoulder reposition available. The doctor uses the most suitable technique and pays close attention not to damage vital structures of the joint and nearby tissues. Close reduction is performed first and in case it fails the patients must undergo surgical open reduction of the injured shoulder. The arm is then put in a sling for several days. After the treatment the patient's shoulder is once more exposed to X-ray examination to confirm proper reposition.







Your thoughts on this
Loading...