Wisdom teeth are the third molars at the back of the mouth. They are the last teeth to grow and they usually grow between ages 17 and 25. People have four wisdom teeth, two in the lower jaw and two in the upper jaw, but they do not always grow out. They may remain inside the gums because there is not enough room for them in the jaw or they grow at an abnormal angle. When this happens, it is called impacted wisdom teeth.
Impacted wisdom teeth may or may not cause problems. If they do, it is usually pain, inflammation or other dental complications, and the tooth needs to be removed. Some dentists even recommend removing one or all of the impacted wisdom teeth even if they are not causing any problems, just to be on the safe side and prevent complications.
Causes of impacted wisdom teeth
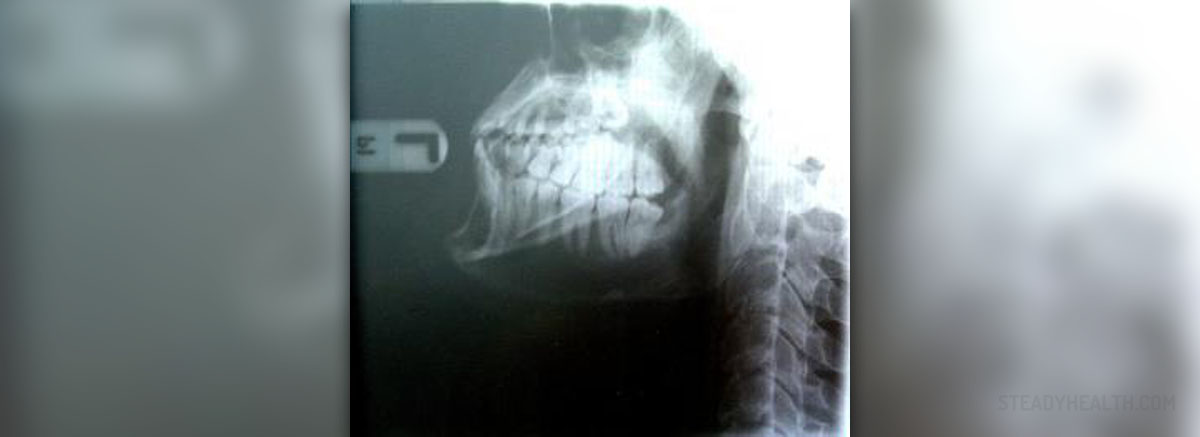
When a wisdom tooth does not have enough room to erupt, it gets impacted. It can partially grow and its crown is then visible, or it can be fully impacted. The tooth may grow towards the adjacent tooth, which is the second molar, in an angle towards the back of the mouth, it can look as if it is lying down in the jawbone or it can be in a perfectly normal position but unable to grow out.
Symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth
An impacted tooth does not necessarily cause any symptoms. However, if it gets infected, if it pushes against the adjacent tooth or damages other teeth, the symptoms usually include pain, which can be very severe, swollen, red, tender and bleeding gums, swelling around the jaw which can be seen from the outside, bad breath along with a foul taste in the mouth, and headache. In case, one of the upper wisdom teeth is impacted, the pain may mimic the symptoms of a sinus infection.
Impacted tooth is not visible without an X-ray, so when a patient complains about pain and swelling behind his or her last molar, the dentist will probably order this test, which enables to see the angle of the tooth and possible infections and inflammations.
Complications of impacted teeth may include tooth decay, cysts, gum disease and damage to the surrounding teeth.
Treatment
An impacted wisdom tooth that is causing pain, swelling and inflammation is usually removed or extracted by an oral surgeon. In case there is an infection, the doctor will probably prescribe a course of antibiotics as well.
As for the asymptomatic impacted teeth, which show no symptoms and cause no problems, experts do not seem to agree on the subject. Some claim that they need to be left alone while others believe that it is better to extract them before they start causing problems, because, according to them, they eventually will.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...