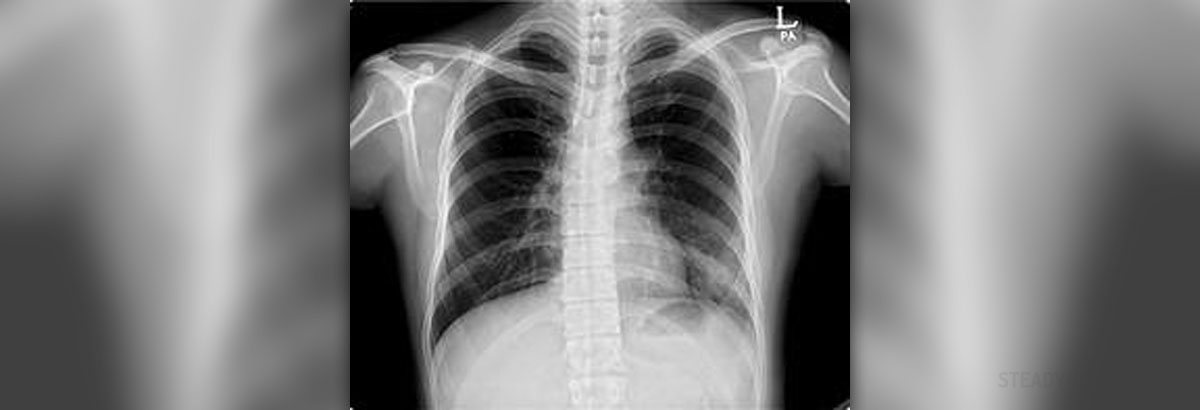
A person whose spine does not look like a letter “I” but rather like letters “S” or “C” is considered to be suffering from a certain condition called scoliosis. Scoliosis is a sideway curative of the spine. Due to this turning of the spine, one shoulder, scapula or hip may appear to be higher than the other. There are three types of scoliosis and idiopathic is named like that because the actual cause is unknown. Depending on the degree of the curve, the frequency of scoliosis varies among the patients. For instance, curves measured of at least 10 degrees are seen in 1.5% to 3% of the population, while curve higher than 30 degrees are seen in no more than 0.3% of the population. Both boys and girls can be affected by scoliosis, the condition is somewhat more common among girls.
What is adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Of all the types of scoliosis, idiopathic scoliosis occurs in 85% of all cases and it is considered to be the most common. 3% of all children aged between 10 and 15 are diagnosed with scoliosis. When cause of scoliosis is considered, it is unknown in almost all cases and that is why it is called idiopathic scoliosis. In other cases, the doctors may suspect of something. For instance, if more family members suffer from it, than there is probably a genetic component which is involved. Scoliosis can occur at any age but adolescent scoliosis occurs after the age of 10. It is also a lot more common than juvenile of infant scoliosis. Unlike most of the other health conditions, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis does not cause any pain, neurological dysfunction or respiratory problems and that is why some cases are hard to identify. It is usually the cosmetic appearance of the back that is the main concern for both the patients and the parents.
Primary care evaluation
There are a lot of schools which have scoliosis screening being done there. In schools where that is not the case, the biggest responsibility lies with primary care providers. They are essential for the early detection and treatment. Evaluating the spine of the children is very important part of making a diagnose and that is done with a comprehensive physical evaluation. The doctor will usually ask the child to bend forward which will allow the doctor to see if there are any deformities. Such an examination is known as Adam’s forward bend test. The doctor will also need to check for any limb-length discrepancies, abnormal neurological findings or some other causes which may have caused scoliosis to occur. In order for the proper diagnosis to be made, the doctor will order an x-ray exam. Thanks to the x-ray the doctor will be able to measure the degree of the curve. Scoliosis is not a problem that can be left untreated and all the curves which are 50 degrees of more are most likely to cause problems in the long term. It is not uncommon for the progressive deterioration of the scoliosis curve to occur. If that happens, a patient may end up suffering from diminished lung capacity or perhaps develop some sort of a restrictive lung disease. There is no one treatment for all cases of scoliosis and the proper treatment will depend on the kind and degree of the curve, the age of the patient and the number of remaining growth years the patient has until he or she reaches skeletal maturity. It is important to know that there are nonsurgical treatment options and surgical treatment options. Observation is one of the nonsurgical treatments and this option is a good one when the curve is a mild one, which means that it is less than 20 degrees. Observation is also the best option in cases where the child is near skeletal maturity. The child will need to go on regular checkups in order for the doctor to make sure that the curve is not getting worse. Bracing is another option and it is supposed to prevent the curves from getting worse. Bracing is mainly used in cases where the patient is still growing and the degree of the curve is between 25 and 45. Underarm brace is the most commonly used brace. Surgery is recommended in situations where the curve is more than 45 degrees and the child is still growing. Surgery is also an option in patients who have reached skeletal maturity but the curve is higher than 50 degrees.
Prognosis
In almost all cases where surgery was used, the patients will experience no pain once they have recovered from the procedure. It will take between 6 and 9 months until the patient will be able to return to most sporting activities. Most means that a person should not take part in any contact sport such as rugby or football for even a longer time. This is mainly because of the permanent limitation of the spine movement after the surgery.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...