Hypokalemia is one many imbalances of electrolytes in the body characterized by low level of potassium. This mineral is of great importance for practically all cells in the body, especially the heart cells, skeletal and smooth muscles. We generally introduce sufficient amounts of potassium on a daily basis and fulfill widely accepted recommendations. Potassium is found in all meats, some types of fish and various fruits and vegetables. Plenty of potassium is also found in legumes and dairy products.
However, under certain circumstances, particularly if one is suffering from certain medical conditions or takes some medications potassium may be expelled from the body much more than it is supposed to. This leads to hypokaliemia and all the associated complications.
Potassium Chloride for Hypokalemia
Potassium chloride is prescribed in people suffering from severe hypokalemia. The drug should never be taken prior to consultation with a health care provider since too much potassium may also be detrimental to the body.
As it has already been mentioned the abnormally low level of potassium is closely connected with some illnesses, intake of certain drugs and is additionally a potential complication of prolonged vomiting.
First and utmost, the drug is never prescribed before patients and the diseases they are currently suffering from are thoroughly evaluated. For instance, the drug is contraindicated in people suffering from kidney failure and Addison’s disease.
Furthermore, it is never administered when there are severe burns or complex tissue injuries. Dehydration, regular intake of some diuretics as well as hyperkalemia (excess of potassium) all are several more contraindications for potassium chloride.
Additional precautionary measures are taken in case the person is already suffering from some heart disease or hypertension, if there is a blockage in the stomach or the intestine and if one has a history of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, both of which lead to chronic diarrhea.
Tablets or capsules are taken whole and should never be crushed or damaged in any way. This prevents the release of too much active substance within the short period of time which might result in adverse effects. The drug can be taken with food or after a meal.
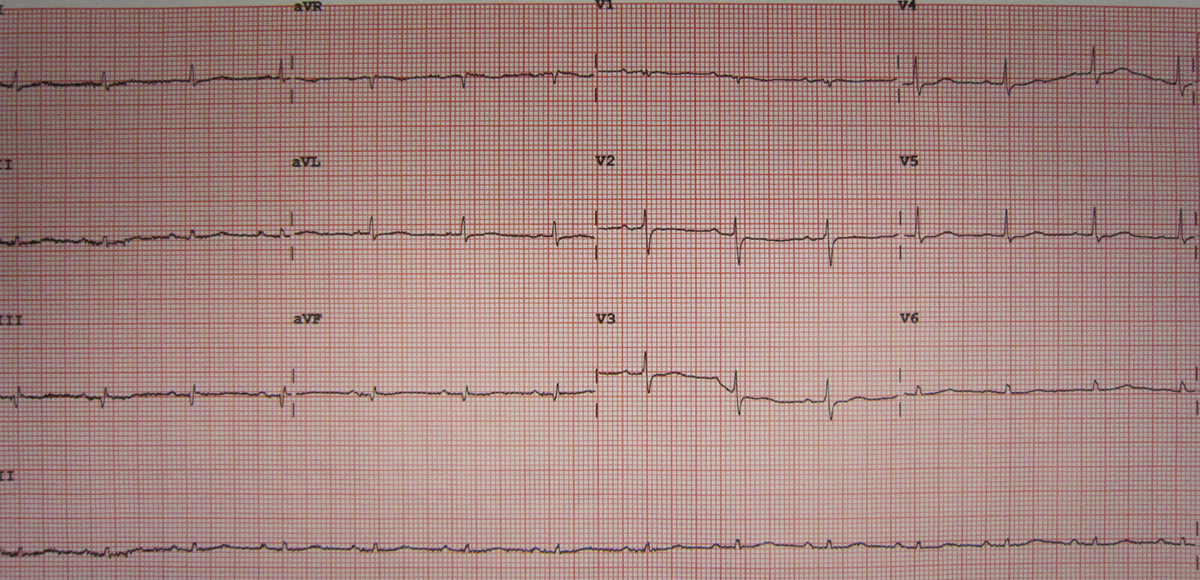
The dose of potassium chloride must be carefully calculated. During the treatment patients undergo regular blood tests which measure the level of the mineral in the blood. If there is a need, the dose is adjusted. One more test that should be performed while one is taking potassium chloride is electrocardiography. Namely, the heart rate and activity of the heart muscle may change in the specific way if there is too much or not enough potassium in the body and these changes are easily recorded with EKG.
In the end, since potassium chloride belongs to FDA pregnancy category C it is unclear whether it might cause damage to the fetus and this is why it is supposed to be avoided. Also, the drug should not be taken during the period of breastfeeding.
Side Effects of Potassium Chloride
First of all, allergic reactions to potassium chloride will never occur if the drug is avoided by sensitive individuals. Still, in case one does not know that he/she is allergic to potassium chloride and develops an allergic reaction prompt medical attention is a must no matter if the allergic reaction is only in the form of hives. Allergic reactions are unpredictable and may easily progress from mild into rather severe forms such as life-threatening anaphylaxis.
Naturally, there are other side effects apart from allergic reactions. The drug may precipitate confusion and anxiety making one feels as if he/she is going to lose consciousness.
Additionally, there can be extreme thirst and frequent /increased urination. Leg discomfort along with muscle weakness or limp sensation may occur as well.
One of the most severe adverse effects is uneven heartbeat which can be even fatal. On the other hand, numbness/tingling sensation in the hands/feet or around the mouth never cause any serious problems and may even withdraw on their own.
And finally, potassium chloride may precipitate vomiting, diarrhea, black/tarry stools accompanied by severe abdominal pain.
Fortunately, most adverse effects are well-tolerated and in the form of mild nausea, occasional diarrhea and transient tingling in the hands or feet.
By following doctor’s orders one will successfully avoid overdose. If, however, one takes more drug than prescribed, he/she must seek emergency medical attention without hesitation. Increased concentration of potassium in the blood soon progresses into confusion, weak and shallow breathing and slow, uneven heartbeat. Convulsions, heavy feeling in the arms and legs or a sensation that the one might faint are also a possibility. The sooner the person is hospitalized, the greater are the chances that the abnormal level of potassium will be timely corrected and potential complications avoided.
Individuals who are prescribed potassium chloride should abstain from potassium supplements or any product which contains potassium. Both, intake of prescribed drug and products containing potassium only increase the risk of adverse effects.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...