
Low levels of potassium are prone to cause series of health problems. Deficiency of potassium often causes symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, uneven heartbeats and hypertension. Typical potassium levels are between 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L; at least 95% of the body's potassium is found inside cells and the rest of it is in the blood. It is one of the essential minerals vital for maintaining normal functions of the muscles and nerves. It also assists to uphold cell electrical potential, electrolyte balance and acid-base balance in the body. It contributes nerve impulse transmission and contractions of the muscles, including the heart.
An average person needs around 3500 milligrams of potassium daily and meeting the minimum requirement is not difficult with a healthy nutrition and regular intake of a variety of foods: fresh fruits and vegetables, spinach, mushrooms, beef, chicken and fish, such as salmon, flounder, cod, and sardines.
General causes
Low potassium levels may be caused by a number of reasons, including some medical conditions. Even the minor changes in potassium levels may affect normal body functions. Low levels of potassium form a condition known as hypokalemia, while increased levels of potassium may lead to hyperkalemia. People with kidney problems or severe infections could suffer from increased potassium levels.
Four major causes
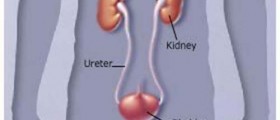
Loss of potassium from kidneys: acute or chronic renal failure or renal tubular acidosis, as well as the other kidney-related conditions, can cause low potassium levels. Kidneys may, in some case, excrete more potassium because of the hyper production of the aldosterone hormone. This happens when the levels of aldosterone hormone are greater than normal owing to adrenal tumors or renal artery stenosis. Cushing’s syndrome or certain medications can also affect high corticosteroid levels and cause potassium deficiency as well.
Loss of potassium from gastrointestinal tract: gastro-intestinal problems such as diarrhea or vomiting can result in an excessive lost of potassium. Hypokalemia may also occur from an excessive use of laxatives, some types of colon polyp and as a side-effect of ileostomy bowel surgery.Loss of potassium due to medications: certain medical treatments (especially those that involve diuretics, insulin, Prednisone, amphotericin B and amino glycosides) may affect potassium levels in body. This especially holds for medications used in the treatment of emphysema or asthma: steroids, bronchodilators or theophylline.
Poor diet: inadequate nutrition may often be the cause of low potassium levels. Dropping the level below 2.5 mEq/L could endanger patients life and needs professional attention. However, in less severe hypokalemia cases patient can use potassium supplements and boost the intake of potassium enriched foods to restore normal levels.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...