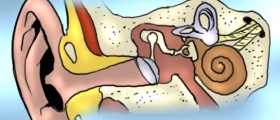
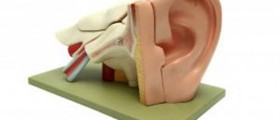
The eardrum, medically called the tympanic membrane, is the thin membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear. When the sound waves that originate from the environment strike the tympanic membrane, it vibrates. The membrane subsequently transfers these vibrations to the inner structure of the ear, which then converts it to nerve signals which the brain can interpret and translate into sounds that you hear.
In addition to this important function, the eardrum also serves as a protective barrier for the middle ear, to reduce the risk that potentially harmful outside factors will reach it.
When the eardrum is punctured or perforated, that means there is a small opening through which a wide variety bacteria may travel and infect the middle ear.
The eardrum can suffer damage as the result of physical trauma such as a direct injury, or as the result of so-called barotraumas — which is essentially damage caused by high levels of pressure. Some people insert q-tips, pencils, bobby pins or fingers into the ear canal in an attempt to clean them, and thus risk damaging the eardrum.
Infections of the ear can also cause a rupture in the eardrum due to the fluid build up, but the reverse scenario is possible as well — a ruptured eardrum can make way for the bacteria that then cause an infection.
- The affectation of tympanic membrane in 47.8% of cases of ear trauma found in study was marginally higher than the frequency of 44.0% reported over a decade ago.
- Traumatic injuries are often sporadic in occurrence and are mostly unplanned events thus patients who sustain such injuries consult the nearest available doctor for initial evaluation.
- The common presenting symptoms of patients were hearing loss (64.2%), tinnitus (50.9%) and ear ache (41.5%).
- The outcome of the injury in terms of healing of the perforation was adjudged good in majority of the ears, however 19.7% had poor outcomes. The outcome may be related to the location of the perforation which could be either in the antero-inferior or in the postero-superior quadrant.
Symptoms of a Ruptured Eardrum
When damage to the eardrum occurs, possible symptoms may include:
- Pain
- Discharge from the ear that can be in the form of pus, clear fluid, or fluid with traces of blood
- Buzzing in the ear
- Facial weakness
- Dizziness, since the ear plays an important role in allowing your body to maintain a sense of balance
- Worst of all, partial or complete hearing loss.
The pain might subside after the drainage of the fluids that have built up in the ear.
Ruptured Eardrum: Diagnosis and Treatment
Doctors are usually able to diagnose a ruptured eardrum when the patient reports the trauma inflicted to the ear and when he or she describes the symptoms in detail. While seeing an ear, nose, and throat specialist is always good, family doctors, too, can diagnose ruptured eardrums. The doctor may examine the ear with an instrument called an otoscope and they may also perform an auditory test to determine the level of hearing loss.
A ruptured or perforated eardrum usually heals by itself after approximately two months, so the treatment in most cases aims to relieve the pain and discomfort and to prevent a possible infection. Antibiotics may be prescribed as a prevention against infections and they may come in the form of oral pills or ear drops.
Painkillers, most of them available over the counter, can be taken for the pain that usually accompanies the rupture of an eardrum.
In some cases when the eardrum does not heal by itself, a surgical procedure called a tympanoplasty may be required.
As for the at-home treatment, the best thing to do is to keep the ear warm which helps with the pain and discomfort. The air should be clean and dry during the healing and recovery. Cotton balls should be inserted gently into the affected ear while showering and shampooing to keep the water and foam away from the ear.
Ruptured Eardrum: Prognosis and Complications
A ruptured eardrum usually takes up to two months to heal and in most cases the hearing loss is temporary. Possible complications of this condition include an ear infection, spreading of the infection to the surrounding bones and tissues, and permanent hearing loss.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...