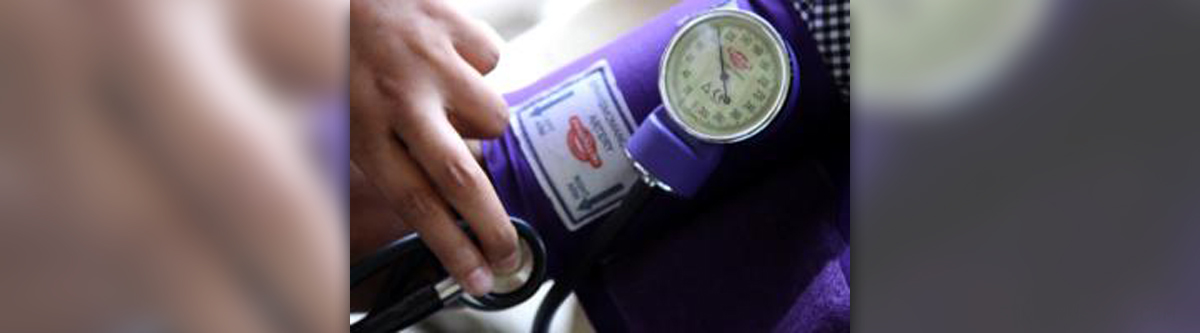
High blood pressure is a medical condition also known under the name hypertension. This condition is a serious health concern that is best described as the abnormally elevated value of pressure at which blood gets pushed against the arterial walls. The blood pressure results from the heart’s contractions. The heart pumps the blood, which is carried away to the rest of the body through the network of arteries. The most common consequence of hypertension is a heart disease. People usually believe that hypertension affects only older population. However, this serious health problem can start very early and develop undetected for decades. High blood pressure is often called “the silent killer”, because symptoms develop so gradually that patients usually seek medical help only when the vital functions are damaged. The only way to detect this problem on time is to have regular blood pressure measurements.
Epidemiology
It is estimated that about 26% of population all around the world suffers from some type of hypertension at each given point of time. The condition is equally common in both developed and undeveloped countries. Hypertension is more common in black people and Native Americans and less in caucasians and Mexican Americans. People having a family history of hypertension are more likely to develop the condition. The risk drastically increases with the age. Women are more likely to develop hypertension after menopause, while men are most affected through early middle age. Overweight, obese and physically inactive people are at the highest risk, since their artery walls suffer additional pressure.
Complications
High blood pressure causes the patient’s heart to pump harder and arteries carry the blood that is moving under the drastically increased pressure. This puts additional stress on the heart and arteries that gradually became weaker. This process affects the patient’s organs and general health. The condition is very risky for pregnant women as it is associated with some severe complications, such as low birth-weight or premature birth.
Classification of high blood pressure
Blood pressure is classified based on the readings in the doctor’s office. During each heartbeat, blood pressure varies between maximum and minimum pressure - systolic and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure is the pressure of blood against the artery walls while diastolic pressure is the pressure between beats. Patients with blood pressures higher than 120/80 mmHg are diagnosed with prehypertension. Stage 1 hypertension is described by measurements of a systolic pressure ranging from 140 to 159 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure ranging from 90 to 99 mm Hg. Stage 2 hypertension, the most severe type, is characterized by the systolic pressure of 160 mm Hg or higher or a diastolic pressure of 100 mm Hg or higher.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...